Ondansetron reverses antihypersensitivity from clonidine in rats after peripheral nerve injury: role of γ-aminobutyric acid in α2-adrenoceptor and 5-HT3 serotonin receptor analgesia
- PMID: 22722575
- PMCID: PMC3496934
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318260d381
Ondansetron reverses antihypersensitivity from clonidine in rats after peripheral nerve injury: role of γ-aminobutyric acid in α2-adrenoceptor and 5-HT3 serotonin receptor analgesia
Abstract
Introduction: Monoaminergic pathways, impinging an α2-adrenoceptors and 5-HT3 serotonin receptors, modulate nociceptive transmission, but their mechanisms and interactions after neuropathic injury are unknown. Here we examine these interactions in rodents after nerve injury.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats following L5-L6 spinal nerve ligation (SNL) were used for either behavioral testing, in vivo microdialysis for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and acetylcholine release, or synaptosome preparation for GABA release.
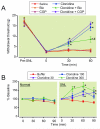
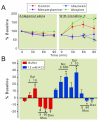
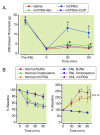
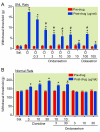
Results: Intrathecal administration of the α2-adrenoceptor agonist (clonidine) and 5-HT3 receptor agonist (chlorophenylbiguanide) reduced hypersensitivity in SNL rats via GABA receptor-mediated mechanisms. Clonidine increased GABA and acetylcholine release in vivo in the spinal cord of SNL rats but not in normal rats. Clonidine-induced spinal GABA release in SNL rats was blocked by α2-adrenergic and nicotinic cholinergic antagonists. The 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron decreased and chlorophenylbiguanide increased spinal GABA release in both normal and SNL rats. In synaptosomes from the spinal dorsal horn of SNL rats, presynaptic GABA release was increased by nicotinic agonists and decreased by muscarinic and α2-adrenergic agonists. Spinally administered ondansetron significantly reduced clonidine-induced antihypersensitivity and spinal GABA release in SNL rats.
Conclusion: These results suggest that spinal GABA contributes to antihypersensitivity from intrathecal α2-adrenergic and 5-HT3 receptor agonists in the neuropathic pain state, that cholinergic neuroplasticity after nerve injury is critical for α2-adrenoceptor-mediated GABA release, and that blockade of spinal 5-HT3 receptors reduces α2-adrenoceptor-mediated antihypersensitivity via reducing total GABA release.
Figures



Similar articles
-
alpha2-Adrenoceptor activation by clonidine enhances stimulation-evoked acetylcholine release from spinal cord tissue after nerve ligation in rats.Anesthesiology. 2005 Mar;102(3):657-62. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200503000-00027. Anesthesiology. 2005. PMID: 15731607
-
Lack of analgesic efficacy of spinal ondansetron on thermal and mechanical hypersensitivity following spinal nerve ligation in the rat.Brain Res. 2010 Sep 17;1352:83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.07.020. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20637741 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal nerve ligation increases alpha2-adrenergic receptor G-protein coupling in the spinal cord.Brain Res. 2005 Mar 15;1038(1):76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.01.016. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15748875
-
Presynaptic Adrenoceptors.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:185-245. doi: 10.1007/164_2024_714. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38755350 Review.
-
Analgesic synergy between opioid and α2 -adrenoceptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):388-402. doi: 10.1111/bph.12695. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24641506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Descending projection neurons in the primary sensorimotor cortex regulate neuropathic pain and locomotion in mice.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 3;16(1):5918. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61164-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40610407 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Spinal 5-HT3 Receptor and Spinal Dorsal Horn Neuronal Excitability Alleviates Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Dec;59(12):7253-7264. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03034-8. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36168076
-
Baicalin relieves neuropathic pain by regulating α2-adrenoceptor levels in rats following spinal nerve injury.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2684-2690. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9019. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765762 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin-4 receptor expression in the rostral ventromedial medulla involved in modulation of nociception in transgenic mice.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Apr;33(2):195-198. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1096-9. Epub 2013 Apr 17. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23592129
-
Tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptor currents in NCB-20 cells.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;22(5):585-595. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.5.585. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30181705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melzack R, Wall PD. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science. 1965;150:971–9. - PubMed
-
- Millan MJ. Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;66:355–474. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Shipley MT, Chouvet G, Ennis M, van Bockstaele E, Pieribone V, Shiekhattar R, Akaoka H, Drolet G, Astier B, et al. Afferent regulation of locus coeruleus neurons: anatomy, physiology and pharmacology. Prog Brain Res. 1991;88:47–75. - PubMed
-
- Pertovaara A. Noradrenergic pain modulation. Prog Neurobiol. 2006;80:53–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
