Novel late-onset Alzheimer disease loci variants associate with brain gene expression
- PMID: 22722634
- PMCID: PMC3398432
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182605801
Novel late-onset Alzheimer disease loci variants associate with brain gene expression
Abstract
Objective: Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of late-onset Alzheimer disease (LOAD) identified 9 novel risk loci. Discovery of functional variants within genes at these loci is required to confirm their role in Alzheimer disease (AD). Single nucleotide polymorphisms that influence gene expression (eSNPs) constitute an important class of functional variants. We therefore investigated the influence of the novel LOAD risk loci on human brain gene expression.
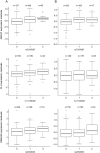
Methods: We measured gene expression levels in the cerebellum and temporal cortex of autopsied AD subjects and those with other brain pathologies (∼400 total subjects). To determine whether any of the novel LOAD risk variants are eSNPs, we tested their cis-association with expression of 6 nearby LOAD candidate genes detectable in human brain (ABCA7, BIN1, CLU, MS4A4A, MS4A6A, PICALM) and an additional 13 genes ±100 kb of these SNPs. To identify additional eSNPs that influence brain gene expression levels of the novel candidate LOAD genes, we identified SNPs ±100 kb of their location and tested for cis-associations.
Results: CLU rs11136000 (p = 7.81 × 10(-4)) and MS4A4A rs2304933/rs2304935 (p = 1.48 × 10(-4)-1.86 × 10(-4)) significantly influence temporal cortex expression levels of these genes. The LOAD-protective CLU and risky MS4A4A locus alleles associate with higher brain levels of these genes. There are other cis-variants that significantly influence brain expression of CLU and ABCA7 (p = 4.01 × 10(-5)-9.09 × 10(-9)), some of which also associate with AD risk (p = 2.64 × 10(-2)-6.25 × 10(-5)).
Conclusions: CLU and MS4A4A eSNPs may at least partly explain the LOAD risk association at these loci. CLU and ABCA7 may harbor additional strong eSNPs. These results have implications in the search for functional variants at the novel LOAD risk loci.
Figures
Comment in
-
For Alzheimer disease GWAS, pulling needles from the haystack is just the first step.Neurology. 2012 Jul 17;79(3):204-5. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318260581d. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Neurology. 2012. PMID: 22722635 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 2009;41:1094–1099 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AG006576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006375/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 032990/PHS HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024151/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
