Compartmentalized calcium dynamics in a C. elegans interneuron encode head movement
- PMID: 22722842
- PMCID: PMC3393794
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11081
Compartmentalized calcium dynamics in a C. elegans interneuron encode head movement
Abstract
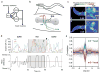
The confinement of neuronal activity to specific subcellular regions is a mechanism for expanding the computational properties of neurons. Although the circuit organization underlying compartmentalized activity has been studied in several systems, its cellular basis is still unknown. Here we characterize compartmentalized activity in Caenorhabditis elegans RIA interneurons, which have multiple reciprocal connections to head motor neurons and receive input from sensory pathways. We show that RIA spatially encodes head movement on a subcellular scale through axonal compartmentalization. This subcellular axonal activity is dependent on acetylcholine release from head motor neurons and is simultaneously present and additive with glutamate-dependent globally synchronized activity evoked by sensory inputs. Postsynaptically, the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor GAR-3 acts in RIA to compartmentalize axonal activity through the mobilization of intracellular calcium stores. The compartmentalized activity functions independently of the synchronized activity to modulate locomotory behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
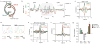


Similar articles
-
A Gate-and-Switch Model for Head Orientation Behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans.eNeuro. 2018 Dec 10;5(6):ENEURO.0121-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0121-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30627635 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic Sensorimotor Integration Regulates Olfactory Steering.Neuron. 2018 Jan 17;97(2):390-405.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29290549 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting a circuit for olfactory behaviour in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nature. 2007 Nov 1;450(7166):63-70. doi: 10.1038/nature06292. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17972877
-
Mechanosensation circuitry in Caenorhabditis elegans: A focus on gentle touch.Peptides. 2015 Jun;68:164-74. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.12.004. Epub 2014 Dec 25. Peptides. 2015. PMID: 25543196 Review.
-
Temperature signaling underlying thermotaxis and cold tolerance in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Neurogenet. 2020 Sep-Dec;34(3-4):351-362. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1734001. Epub 2020 Apr 21. J Neurogenet. 2020. PMID: 32316810 Review.
Cited by
-
Associative learning drives longitudinally graded presynaptic plasticity of neurotransmitter release along axonal compartments.Elife. 2022 Mar 14;11:e76712. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76712. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35285796 Free PMC article.
-
A Gate-and-Switch Model for Head Orientation Behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans.eNeuro. 2018 Dec 10;5(6):ENEURO.0121-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0121-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30627635 Free PMC article.
-
Forgetting generates a novel state that is reactivatable.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 11;8(6):eabi9071. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abi9071. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35148188 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Coding of Thermal Preferences in the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.eNeuro. 2020 Jun 26;7(3):ENEURO.0414-19.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0414-19.2020. Print 2020 May/Jun. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32253198 Free PMC article.
-
A Computational Model Based on Multi-Regional Calcium Imaging Represents the Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in a Caenorhabditis elegans Sensory Neuron.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 10;12(1):e0168415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168415. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28072834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Euler T, Detwiler PB, Denk W. Directionally selective calcium signals in dendrites of starburst amacrine cells. Nature. 2002;418:845–852. - PubMed
-
- Borst A, Euler T. Seeing things in motion: Models, circuits, and mechanisms. Neuron. 2011;71 :974–994. - PubMed
-
- Rall W, Shepherd GM, Reese TS, Brightman MW. Dendrodendritic synaptic pathway for inhibition in the olfactory bulb. Exp Neurol. 1966;14:44–56. - PubMed
-
- White JG, Southgate E, Thomson JN, Brenner S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B. 1986;314:1–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

