Site-specific DICER and DROSHA RNA products control the DNA-damage response
- PMID: 22722852
- PMCID: PMC3442236
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11179
Site-specific DICER and DROSHA RNA products control the DNA-damage response
Abstract
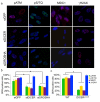
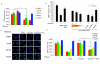
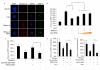
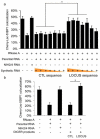
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are involved in an increasingly recognized number of cellular events. Some ncRNAs are processed by DICER and DROSHA RNases to give rise to small double-stranded RNAs involved in RNA interference (RNAi). The DNA-damage response (DDR) is a signalling pathway that originates from a DNA lesion and arrests cell proliferation3. So far, DICER and DROSHA RNA products have not been reported to control DDR activation. Here we show, in human, mouse and zebrafish, that DICER and DROSHA, but not downstream elements of the RNAi pathway, are necessary to activate the DDR upon exogenous DNA damage and oncogene-induced genotoxic stress, as studied by DDR foci formation and by checkpoint assays. DDR foci are sensitive to RNase A treatment, and DICER- and DROSHA-dependent RNA products are required to restore DDR foci in RNase-A-treated cells. Through RNA deep sequencing and the study of DDR activation at a single inducible DNA double-strand break, we demonstrate that DDR foci formation requires site-specific DICER- and DROSHA-dependent small RNAs, named DDRNAs, which act in a MRE11–RAD50–NBS1-complex-dependent manner (MRE11 also known as MRE11A; NBS1 also known as NBN). DDRNAs, either chemically synthesized or in vitro generated by DICER cleavage, are sufficient to restore the DDR in RNase-A-treated cells, also in the absence of other cellular RNAs. Our results describe an unanticipated direct role of a novel class of ncRNAs in the control of DDR activation at sites of DNA damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DICER, DROSHA and DNA damage response RNAs are necessary for the secondary recruitment of DNA damage response factors.J Cell Sci. 2016 Apr 1;129(7):1468-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.182188. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 26906421 Free PMC article.
-
BRG1 and SMARCAL1 transcriptionally co-regulate DROSHA, DGCR8 and DICER in response to doxorubicin-induced DNA damage.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 Sep;1860(9):936-951. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 28716689
-
Damage-induced lncRNAs control the DNA damage response through interaction with DDRNAs at individual double-strand breaks.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Dec;19(12):1400-1411. doi: 10.1038/ncb3643. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 29180822 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs: emerging key players in DNA double-strand break repair.Sci China Life Sci. 2013 Oct;56(10):933-6. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4552-7. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Sci China Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24026293 Review.
-
A direct role for small non-coding RNAs in DNA damage response.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;24(3):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24156824 Review.
Cited by
-
Serial interactome capture of the human cell nucleus.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 4;7:11212. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11212. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27040163 Free PMC article.
-
Regulators of homologous recombination repair as novel targets for cancer treatment.Front Genet. 2015 Mar 20;6:96. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00096. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25852742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs in DNA damage response.Am J Cancer Res. 2012;2(6):658-75. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Am J Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23226613 Free PMC article.
-
Low dose rate γ-irradiation protects fruit fly chromosomes from double strand breaks and telomere fusions by reducing the esi-RNA biogenesis factor Loquacious.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 3;5(1):905. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03885-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36057690 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Reg IV and Hgf mRNAs by Intermittent Hypoxia via Downregulation of microRNA-499 in Cardiomyocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 17;23(20):12414. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012414. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293268 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

