Butein inhibits ethanol-induced activation of liver stellate cells through TGF-β, NFκB, p38, and JNK signaling pathways and inhibition of oxidative stress
- PMID: 22722906
- PMCID: PMC3575555
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-012-0619-7
Butein inhibits ethanol-induced activation of liver stellate cells through TGF-β, NFκB, p38, and JNK signaling pathways and inhibition of oxidative stress
Abstract
Background: Butein has been reported to prevent and partly reverse liver fibrosis in vivo; however, the mechanisms of its action are poorly understood. We, therefore, aimed to determine the antifibrotic potential of butein.
Methods: We assessed the influence of the incubation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and hepatoma cells (HepG2) with butein on sensitivity to ethanol- or acetaldehyde-induced toxicity; the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS); the expression of markers of HSC activation, including smooth muscle α-actin (α-SMA) and procollagen I; and the production of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), metalloproteinases-2 and -13 (MMP-2and MMP-13), and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). The influence of butein on intracellular signals in HSCs; i.e., nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) induced by ethanol was estimated.
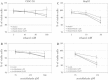
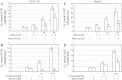
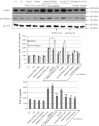
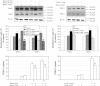
Results: Butein protected HSCs and HepG2 cells against ethanol toxicity by the inhibition of ethanol- or acetaldehyde-induced production of ROS when cells were incubated separately or in co-cultures; butein also inhibited HSC activation measured as the production of α-SMA and procollagen I. As well, butein downregulated ethanol- or acetaldehyde-induced HSC migration and the production of TGF-β, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2; decreased the activity of MMP-2; and increased the activity of MMP-13. In ethanol-induced HSCs, butein inhibited the activation of the p38 MAPK and JNK transduction pathways as well as significantly inhibiting the phosphorylation of NF κB inhibitor (IκB) and Smad3.
Conclusions: The results indicated that butein inhibited ethanol- and acetaldehyde-induced activation of HSCs at different levels, acting as an antioxidant and inhibitor of ethanol-induced MAPK, TGF-β, and NFκB/IκB transduction signaling; this result makes butein a promising agent for antifibrotic therapies.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Zinc supplementation attenuates ethanol- and acetaldehyde-induced liver stellate cell activation by inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and by influencing intracellular signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Aug 1;78(3):301-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.04.009. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19376089
-
Betulin and betulinic acid attenuate ethanol-induced liver stellate cell activation by inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS), cytokine (TNF-α, TGF-β) production and by influencing intracellular signaling.Toxicology. 2011 Feb 27;280(3):152-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.12.006. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Toxicology. 2011. PMID: 21172400
-
Betulin, betulinic acid and butein are inhibitors of acetaldehyde-induced activation of liver stellate cells.Pharmacol Rep. 2011;63(5):1109-23. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70630-2. Pharmacol Rep. 2011. PMID: 22180353
-
Dysregulation of redox pathways in liver fibrosis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Oct 1;311(4):G667-G674. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00050.2016. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27562057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive potential of butein: Current trends and future perspectives.Chem Biol Interact. 2021 Dec 1;350:109699. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109699. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2021. PMID: 34648814 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cytochrome P450 2e1 expression by ethanol: role of oxidative stress-mediated pkc/jnk/sp1 pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Mar 21;4(3):e554. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.78. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23519123 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β signal shifting between tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis in human chronic liver diseases.J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun;49(6):971-81. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0910-2. Epub 2013 Nov 22. J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24263677 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 21;20(23):7260-76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24966597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhus verniciflua Stokes attenuates cholestatic liver cirrhosis-induced interstitial fibrosis via Smad3 down-regulation and Smad7 up-regulation.Anat Cell Biol. 2016 Sep;49(3):189-198. doi: 10.5115/acb.2016.49.3.189. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Anat Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27722012 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of IKKβ/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad via Fuzheng Huayu recipe involves in prevention of nutritional steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Apr;18(4):404-11. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26019805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman SL, Yamasaki G, Wong L. Modulation of transforming growth factor beta receptors of rat lipocytes during the hepatic wound healing response. Enhanced binding and reduced gene expression accompany cellular activation in culture and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:10551–10558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

