Exosomes as biomarker enriched microvesicles: characterization of exosomal proteins derived from a panel of prostate cell lines with distinct AR phenotypes
- PMID: 22723089
- PMCID: PMC3494141
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.014845
Exosomes as biomarker enriched microvesicles: characterization of exosomal proteins derived from a panel of prostate cell lines with distinct AR phenotypes
Abstract
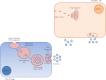
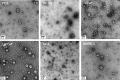
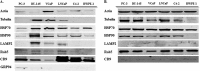
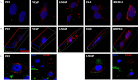
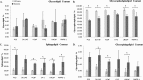
Prostate cancer is the leading type of cancer diagnosed in men. In 2010, ~217,730 new cases of prostate cancer were reported in the United States. Prompt diagnosis of the disease can substantially improve its clinical outcome. Improving capability for early detection, as well as developing new therapeutic targets in advanced disease are research priorities that will ultimately lead to better patient survival. Eukaryotic cells secrete proteins via distinct regulated mechanisms which are either ER/Golgi dependent or microvesicle mediated. The release of microvesicles has been shown to provide a novel mechanism for intercellular communication. Exosomes are nanometer sized cup-shaped membrane vesicles which are secreted from normal and cancerous cells. They are present in various biological fluids and are rich in characteristic proteins. Exosomes may thus have potential both in facilitating early diagnosis via less invasive procedures or be candidates for novel therapeutic approaches for castration resistance prostate cancer. Because exosomes have been shown previously to have a role in cell-cell communication in the local tumor microenvironment, conferring activation of numerous survival mechanisms, we characterized constitutive lipids, cholesterol and proteins from exosomes derived from six prostate cell lines and tracked their uptake in both cancerous and benign prostate cell lines respectively. Our comprehensive proteomic and lipidomic analysis of prostate derived exosomes could provide insight for future work on both biomarker and therapeutic targets for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Figures

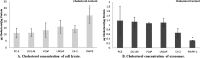
References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Murray T., Xu J., Smigal C., Thun M. J. (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J. Clin. 56, 106–130 - PubMed
-
- Chan J. M., Holick C. N., Leitzmann M. F., Rimm E. B., Willett W. C., Stampfer M. J., Giovannucci E. L. (2006) Diet after diagnosis and the risk of prostate cancer progression, recurrence, and death (United States). Cancer Causes Control 17, 199–208 - PubMed
-
- Bruchovsky N., Klotz L. H., Sadar M., Crook J. M., Hoffart D., Godwin L., Warkentin M., Gleave M. E., Goldenberg S. L. (2000) Intermittent androgen suppression for prostate cancer: Canadian Prospective Trial and related observations. Mol Urol 4, 191–199; discussion 201 - PubMed
-
- Gleave M. E., Goldenberg S. L., Chin J. L., Warner J., Saad F., Klotz L. H., Jewett M., Kassabian V., Chetner M., Dupont C., Van Rensselaer S. (2001) Randomized comparative study of 3 versus 8-month neoadjuvant hormonal therapy before radical prostatectomy: biochemical and pathological effects. J Urol. 166, 500–506; discussion 506–507 - PubMed
-
- Lan C. Y., Huang H., Liu J. H. (2008) [Prognostic value of serum CA(125) level change during chemotherapy post-surgery in patients with advanced epithelial ovarian carcinoma]. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 43, 732–736 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

