The minimal important difference in the 6-minute walk test for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 22723290
- PMCID: PMC3443803
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201203-0480OC
The minimal important difference in the 6-minute walk test for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Rationale: Although commonly used as the primary outcome measure of clinical trials in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), the minimal important difference (MID) of the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) has not been well defined for this population of patients.
Objectives: To estimate the MID in the 6MWT in patients with PAH.
Methods: Study subjects from the clinical trial of tadalafil in PAH, a 16-week, parallel-group, randomized clinical trial of patients who were treatment naive or on background therapy with an endothelin receptor antagonist, were eligible. 6MWT was performed using a standardized protocol. Distributional and anchor-based methods were used to estimate the MID; the latter method used the Physical Component Summary Score (PCS) of the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form (SF-36).
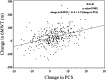
Measurements and main results: Four hundred five subjects were analyzed. Domains of the SF-36 were weakly to modestly associated with 6MWT. Change in the PCS of the SF-36 was most strongly associated with change in 6MWT (r = 0.40, P < 0.001) and thus was selected as the anchor for subsequent anchor-based analyses. Distributional analyses yielded estimates of the MID ranging from 25.1 to 38.5 m, whereas anchor-based analyses yielded an estimate of 38.6 m.
Conclusions: Using both distributional and anchor-based methods, the estimated consensus MID in the 6MWT for PAH is approximately 33 m. These results have important implications for (1) assessing treatment responses from clinical trials and metaanalyses of specific PAH therapy, and (2) sample size calculations for future study design.
Figures
Comment in
-
The 6-minute walk test in pulmonary arterial hypertension: how far is enough?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Sep 1;186(5):396-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201206-1137ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22942342 No abstract available.
-
A call to apply the minimal important difference in pulmonary arterial hypertension beyond the flawed 6-minute-walk test.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Mar 15;187(6):659. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.187.6.659. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23504363 No abstract available.
-
Reply from the authors.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Mar 15;187(6):659. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.187.6.659a. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23614142 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chin KM, Kim NH, Rubin LJ. The right ventricle in pulmonary hypertension. Coron Artery Dis 2005;16:13–18 - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:1573–1619 - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Oudiz RJ, Beardsworth A, Brundage BH, Simonneau G, Ghofrani HA, Sundin DP, Galie N. Tadalafil monotherapy and as add-on to background bosentan in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:632–643 - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Ghofrani HA, Torbicki A, Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Badesch D, Fleming T, Parpia T, Burgess G, Branzi A, et al. Sildenafil citrate therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2148–2157 - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Brundage BH, Ghofrani HA, Oudiz RJ, Simonneau G, Safdar Z, Shapiro S, White RJ, Chan M, Beardsworth A, et al. Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2009;119:2894–2903 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

