Isotype modulates epitope specificity, affinity, and antiviral activities of anti-HIV-1 human broadly neutralizing 2F5 antibody
- PMID: 22723360
- PMCID: PMC3412007
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1200024109
Isotype modulates epitope specificity, affinity, and antiviral activities of anti-HIV-1 human broadly neutralizing 2F5 antibody
Abstract
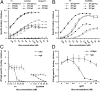
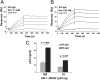
The constant heavy chain (CH1) domain affects antibody affinity and fine specificity, challenging the paradigm that only variable regions contribute to antigen binding. To investigate the role of the CH1 domain, we constructed IgA2 from the broadly neutralizing anti-HIV-1 2F5 IgG1, and compared 2F5 IgA2 and IgG binding affinity and functional activities. We found that 2F5 IgA2 bound to the gp41 membrane proximal external region with higher affinity than IgG1. Functionally, compared with IgG1, 2F5 IgA2 more efficiently blocked HIV-1 transcytosis across epithelial cells and CD4(+) cell infection by R5 HIV-1. The 2F5 IgG1 and IgA2 acted synergistically to fully block HIV-1 transfer from Langerhans to autologous CD4(+) T cells and to inhibit CD4(+) T-cell infection. Epitope mapping performed by screening a random peptide library and in silico docking modeling suggested that along with the 2F5 IgG canonical ELDKWA epitope on gp41, the IgG1 recognized an additional 3D-conformational epitope on the gp41 C-helix. In contrast, the IgA2 epitope included a unique conformational motif on the gp41 N-helix. Overall, the CH1 region of 2F5 contributes to shape its epitope specificity, antibody affinity, and functional activities. In the context of sexually transmitted infections such as HIV-1/AIDS, raising a mucosal IgA-based vaccine response should complement an IgG-based vaccine response in blocking HIV-1 transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

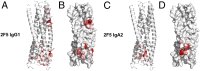
Comment in
-
Immunoglobulin isotype influences affinity and specificity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12272-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209750109. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22826242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Torres M, Casadevall A. The immunoglobulin constant region contributes to affinity and specificity. Trends Immunol. 2008;29:91–97. - PubMed
-
- Bomsel M, et al. Immunization with HIV-1 gp41 subunit virosomes induces mucosal antibodies protecting nonhuman primates against vaginal SHIV challenges. Immunity. 2011;34:269–280. - PubMed
-
- Tudor D, Bomsel M. The broadly neutralizing HIV-1 IgG 2F5 elicits gp41-specific antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in a FcγRI-dependent manner. AIDS. 2011;25:751–759. - PubMed
-
- Alfsen A, Iniguez P, Bouguyon E, Bomsel M. Secretory IgA specific for a conserved epitope on gp41 envelope glycoprotein inhibits epithelial transcytosis of HIV-1. J Immunol. 2001;166:6257–6265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

