Supratentorial hemangioblastoma: clinical features, prognosis, and predictive value of location for von Hippel-Lindau disease
- PMID: 22723428
- PMCID: PMC3408260
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nos133
Supratentorial hemangioblastoma: clinical features, prognosis, and predictive value of location for von Hippel-Lindau disease
Abstract
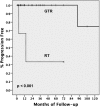
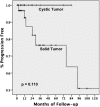
Supratentorial hemangioblastoma is a rare form of hemangioblastoma; little information is available regarding prognosis, treatment, and clinical characteristics, because the available literature is primarily composed of case reports and small case series. Therefore, we performed a systematic review of the literature to analyze clinical characteristics, disease progression, and surgical outcomes with respect to survival for supratentorial hemangioblastomas. The rate of progression-free survival (PFS) was determined using Kaplan-Meier analysis. Differences in categorical factors, including location of tumor and diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease, were analyzed using the Pearson χ(2) test. A total of 106 articles met the search criteria, which combined for a total of 132 patients. Of the patients with supratentorial tumors, 60% had VHL disease, and 31 (84%) of 37 patients with tumors in the sellar/suprasellar region had associated VHL (χ(2), P < .001). Five-year PFS for gross-total resection and subtotal resection were 100% and 53%, respectively (Log rank, P < .01). On the basis of our analysis of the literature on published cases of supratentorial hemangioblastoma, gross-total resection appears to be superior to other treatment modalities in extending PFS. Von Hippel-Lindau disease is positively correlated with supratentorial hemangioblastoma when compared with non-supratentorial CNS hemangioblastomas, particularly when present in the sellar/suprasellar region.
Figures

References
-
- Toyoda H, Seki M, Nakamura H, Inoue Y, Yamano Y, Takaoka K. Intradural extramedullary hemangioblastoma differentiated by MR images in the cervical spine: a case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(4):343–347. doi:10.1097/01.bsd.0000083630.91606.af. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acikalin MF, Oner U, Tel N, Pasaoglu O, Altinel F. Supratentorial hemangioblastoma: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127(9):e382–e384. - PubMed
-
- Hussein MR. Central nervous system capillary haemangioblastoma: the pathologist's viewpoint. Int J Exp Pathol. 2007;88(5):311–324. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2613.2007.00535.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wasenko JJ, Rodziewicz GS. Suprasellar hemangioblastoma in Von Hippel-Lindau disease: a case report. Clin Imaging. 2003;27(1):18–22. doi:10.1016/S0899-7071(02)00537-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jagannathan J, Lonser RR, Smith R, DeVroom HL, Oldfield EH. Surgical management of cerebellar hemangioblastomas in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg. 2008;108(2):210–222. doi:10.3171/JNS/2008/108/2/0210. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

