Entamoeba moshkovskii is associated with diarrhea in infants and causes diarrhea and colitis in mice
- PMID: 22723640
- PMCID: PMC3491739
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis414
Entamoeba moshkovskii is associated with diarrhea in infants and causes diarrhea and colitis in mice
Abstract
Background: Entamoeba moshkovskii is prevalent in developing countries and morphologically indistinguishable from pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica and nonpathogenic Entamoeba dispar. It is not known if E. moshkovskii is pathogenic.
Methods: Mice were intracecally challenged with the trophozoites of each Entamoeba spp. to test the ability to cause diarrhea, and infants in Bangladesh were prospectively observed to see if newly acquired E. moshkovskii infection was associated with diarrhea.
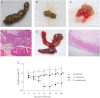
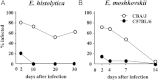
Results: E. moshkovskii and E. histolytica caused diarrhea and weight loss in susceptible mice. E. dispar infected none of the mouse strains tested. In Mirpur, Dhaka, Bangladesh, E. moshkovskii, E. histolytica, and E. dispar were identified in 42 (2.95%), 66 (4.63%), and 5 (0.35%), respectively, of 1426 diarrheal episodes in 385 children followed prospectively from birth to one year of age. Diarrhea occurred temporally with acquisition of a new E. moshkovskii infection: in the 2 months preceding E. moshkvskii-associated diarrhea, 86% (36 of 42) of monthly surveillance stool samples were negative for E. moshkovskii.
Conclusions: E. moshkovskii was found to be pathogenic in mice. In children, the acquisition of E. moshkovskii infection was associated with diarrhea. These data are consistent with E. moshkovskii causing disease, indicating that it is important to reexamine its pathogenicity.
Figures
References
-
- Irusen EM, Jackson TF, Simjee AE. Asymptomatic intestinal colonization by pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica in amebic liver abscess: prevalence, response to therapy, and pathogenic potential. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;14:889–93. - PubMed
-
- Gathiram V, Jackson TF. A longitudinal study of asymptomatic carriers of pathogenic zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica. S Afr Med J. 1987;72:669–72. - PubMed
-
- Vandenberg O, Peek R, Souayah H, et al. Clinical and microbiological features of dientamoebiasis in patients suspected of suffering from a parasitic gastrointestinal illness: a comparison of Dientamoeba fragilis and Giardia lamblia infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2006;10:255–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

