Wnt7A identifies embryonic γ-motor neurons and reveals early postnatal dependence of γ-motor neurons on a muscle spindle-derived signal
- PMID: 22723712
- PMCID: PMC3496251
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1160-12.2012
Wnt7A identifies embryonic γ-motor neurons and reveals early postnatal dependence of γ-motor neurons on a muscle spindle-derived signal
Abstract
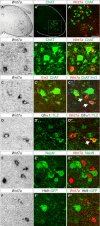
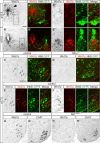
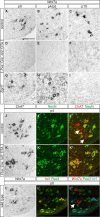
Motor pools comprise a heterogeneous population of motor neurons that innervate distinct intramuscular targets. While the organization of motor neurons into motor pools has been well described, the time course and mechanism of motor pool diversification into functionally distinct classes remains unclear. γ-Motor neurons (γ-MNs) and α-motor neurons (α-MNs) differ in size, molecular identity, synaptic input and peripheral target. While α-MNs innervate extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers to mediate muscle contraction, γ-MNs innervate intrafusal fibers of the muscle spindle, and regulate sensitivity of the muscle spindle in response to stretch. In this study, we find that the secreted signaling molecule Wnt7a is selectively expressed in γ-MNs in the mouse spinal cord by embryonic day 17.5 and continues to molecularly distinguish γ-from α-MNs into the third postnatal week. Our data demonstrate that Wnt7a is the earliest known γ-MN marker, supporting a model of developmental divergence between α- and γ-MNs at embryonic stages. Furthermore, using Wnt7a expression as an early marker of γ-MN identity, we demonstrate a previously unknown dependence of γ-MNs on a muscle spindle-derived, GDNF-independent signal during the first postnatal week.
Figures
References
-
- Arber S, Han B, Mendelsohn M, Smith M, Jessell TM, Sockanathan S. Requirement for the homeobox gene Hb9 in the consolidation of motor neuron identity. Neuron. 1999;23:659–674. - PubMed
-
- Burke RE, Strick PL, Kanda K, Kim CC, Walmsley B. Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1977;40:667–680. - PubMed
-
- Enjin A, Rabe N, Nakanishi ST, Vallstedt A, Gezelius H, Memic F, Lind M, Hjalt T, Tourtellotte WG, Bruder C, Eichele G, Whelan PJ, Kullander K. Identification of novel spinal cholinergic genetic subtypes disclose Chodl and Pitx2 as markers for fast motor neurons and partition cells. J Comp Neurol. 2010;518:2284–2304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
