Hyperpolarizing GABAergic transmission requires the KCC2 C-terminal ISO domain
- PMID: 22723714
- PMCID: PMC3395202
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6089-11.2012
Hyperpolarizing GABAergic transmission requires the KCC2 C-terminal ISO domain
Abstract
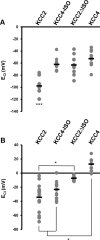
KCC2 is the neuron-specific member of the of K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter gene family. It is also the only member of its family that is active under physiologically normal conditions, in the absence of osmotic stress. By extruding Cl(-) from the neuron under isotonic conditions, this transporter maintains a low concentration of neuronal Cl(-), which is essential for fast inhibitory synaptic transmission by GABA and glycine in the mature nervous system. The other members of this K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter gene family are exclusively swelling-activated. Here we demonstrate that a 15 aa region near the end of the C terminus, unique to KCC2 (termed the ISO domain), is required for KCC2 to cotransport K(+) and Cl(-) out of the neuron under isotonic conditions. We made this discovery by overexpressing chimeric KCC2-KCC4 cDNA constructs in cultured hippocampal neurons prepared from Sprague Dawley rat embryos and assaying neuronal Cl(-) through gramicidin perforated patch-clamp recordings. We found that when neurons had been transfected with a chimeric KCC2 that lacked the unique ISO domain, hyperpolarizing responses to GABA were abolished. This finding indicates that the ISO domain is required for neuronal Cl(-) regulation. Furthermore, we discovered that when KCC2 lacks the ISO domain, it still retains swelling-activated transport, which demonstrates that there are exclusive molecular determinants of isotonic and swelling-induced K(+)-Cl(-) cotransport in neurons.
Figures


References
-
- Bergeron MJ, Gagnon E, Caron L, Isenring P. Identification of key functional domains in the C terminus of the K+-Cl− cotransporters. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:15959–15969. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron MJ, Frenette-Cotton R, Carpentier GA, Simard MG, Caron L, Isenring P. Phosphoregulation of K(+)-Cl(−) cotransporter 4 during changes in intracellular Cl(−) and cell volume. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219:787–796. - PubMed
-
- Blaesse P, Airaksinen MS, Rivera C, Kaila K. Cation-chloride cotransporters and neuronal function. Neuron. 2009;61:820–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
