TRPA1 is a polyunsaturated fatty acid sensor in mammals
- PMID: 22723860
- PMCID: PMC3378573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038439
TRPA1 is a polyunsaturated fatty acid sensor in mammals
Abstract
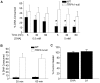
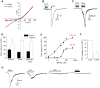
Fatty acids can act as important signaling molecules regulating diverse physiological processes. Our understanding, however, of fatty acid signaling mechanisms and receptor targets remains incomplete. Here we show that Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1), a cation channel expressed in sensory neurons and gut tissues, functions as a sensor of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in vitro and in vivo. PUFAs, containing at least 18 carbon atoms and three unsaturated bonds, activate TRPA1 to excite primary sensory neurons and enteroendocrine cells. Moreover, behavioral aversion to PUFAs is absent in TRPA1-null mice. Further, sustained or repeated agonism with PUFAs leads to TRPA1 desensitization. PUFAs activate TRPA1 non-covalently and independently of known ligand binding domains located in the N-terminus and 5(th) transmembrane region. PUFA sensitivity is restricted to mammalian (rodent and human) TRPA1 channels, as the drosophila and zebrafish TRPA1 orthologs do not respond to DHA. We propose that PUFA-sensing by mammalian TRPA1 may regulate pain and gastrointestinal functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quantification and Potential Functions of Endogenous Agonists of Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug;149(2):433-44.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.011. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25911511
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their endocannabinoid-related metabolites activity at human TRPV1 and TRPA1 ion channels expressed in HEK-293 cells.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 24;13:e19125. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19125. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40151457 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the sensitivity of TRP channels to polyunsaturated fatty acids.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;391(8):833-846. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1507-3. Epub 2018 May 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29736621 Free PMC article.
-
TRPA1 antagonists as potential analgesic drugs.Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Feb;133(2):189-204. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.10.008. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22119554 Review.
-
The transient receptor potential channel TRPA1: from gene to pathophysiology.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Nov;464(5):425-58. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1158-z. Epub 2012 Sep 22. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 23001121 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensory TRP channels: the key transducers of nociception and pain.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;131:73-118. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 25744671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HsTRPA of the Red Imported Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta, Functions as a Nocisensor and Uncovers the Evolutionary Plasticity of HsTRPA Channels.eNeuro. 2018 Feb 6;5(1):ENEURO.0327-17.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0327-17.2018. eCollection 2018 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 29445768 Free PMC article.
-
Early oral nutrition improves postoperative ileus through the TRPA1/CCK1-R-mediated mast cell-nerve axis.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Mar;8(5):179. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.95. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32309326 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-dependent anti-inflammatory signaling actions of unsaturated fatty acids.Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76:79-105. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170341. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24161076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering Subtype-Selective Modulations in TRPA1 Biosensor Channels.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015;13(2):266-78. doi: 10.2174/1570159x1302150525122020. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26411770 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murakami M, Taketomi Y, Miki Y, Sato H, Hirabayashi T, et al. Recent progress in phospholipase A2 research: from cells to animals to humans. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50:152–192. - PubMed
-
- Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science. 2001;294:1871–1875. - PubMed
-
- Gilbertson TA, Fontenot DT, Liu L, Zhang H, Monroe WT. Fatty acid modulation of K+ channels in taste receptor cells: gustatory cues for dietary fat. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:C1203–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

