A global characterization and identification of multifunctional enzymes
- PMID: 22723914
- PMCID: PMC3377604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038979
A global characterization and identification of multifunctional enzymes
Abstract
Multi-functional enzymes are enzymes that perform multiple physiological functions. Characterization and identification of multi-functional enzymes are critical for communication and cooperation between different functions and pathways within a complex cellular system or between cells. In present study, we collected literature-reported 6,799 multi-functional enzymes and systematically characterized them in structural, functional, and evolutionary aspects. It was found that four physiochemical properties, that is, charge, polarizability, hydrophobicity, and solvent accessibility, are important for characterization of multi-functional enzymes. Accordingly, a combinational model of support vector machine and random forest model was constructed, based on which 6,956 potential novel multi-functional enzymes were successfully identified from the ENZYME database. Moreover, it was observed that multi-functional enzymes are non-evenly distributed in species, and that Bacteria have relatively more multi-functional enzymes than Archaebacteria and Eukaryota. Comparative analysis indicated that the multi-functional enzymes experienced a fluctuation of gene gain and loss during the evolution from S. cerevisiae to H. sapiens. Further pathway analyses indicated that a majority of multi-functional enzymes were well preserved in catalyzing several essential cellular processes, for example, metabolisms of carbohydrates, nucleotides, and amino acids. What's more, a database of known multi-functional enzymes and a server for novel multi-functional enzyme prediction were also constructed for free access at http://bioinf.xmu.edu.cn/databases/MFEs/index.htm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
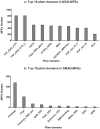

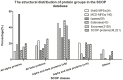
Similar articles
-
AcalPred: a sequence-based tool for discriminating between acidic and alkaline enzymes.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 9;8(10):e75726. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075726. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130738 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Multi-Functional Enzyme with Multi-Label Classifier.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 14;11(4):e0153503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153503. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27078147 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of active sites of enzymes by maximum relevance minimum redundancy (mRMR) feature selection.Mol Biosyst. 2013 Jan 27;9(1):61-9. doi: 10.1039/c2mb25327e. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Mol Biosyst. 2013. PMID: 23117653
-
Review of QSAR models for enzyme classes of drug targets: Theoretical background and applications in parasites, hosts, and other organisms.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(24):2710-23. doi: 10.2174/138161210792389207. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20642430 Review.
-
A global analysis of function and conservation of catalytic residues in enzymes.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 10;295(2):314-324. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.006289. Epub 2019 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31796628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hierarchical classification of protein folds using a novel ensemble classifier.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056499. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437146 Free PMC article.
-
Promiscuous Ribozymes and Their Proposed Role in Prebiotic Evolution.Chem Rev. 2020 Jun 10;120(11):4879-4897. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00620. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Chem Rev. 2020. PMID: 32011135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional alkalophilic α-amylase with diverse raw seaweed degrading activities.AMB Express. 2021 Oct 20;11(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01300-x. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 34669086 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of apolipoprotein using feature selection technique.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 22;6:30441. doi: 10.1038/srep30441. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27443605 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of Natural Language Processing Techniques in Bioinformatics.Comput Math Methods Med. 2015;2015:674296. doi: 10.1155/2015/674296. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015. PMID: 26525745 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jeffery CJ. Multifunctional proteins: examples of gene sharing. Ann Med. 2003;35:28–35. - PubMed
-
- Jeffery CJ. Moonlighting proteins: old proteins learning new tricks. Trends Genet. 2003;19:415–417. - PubMed
-
- Huberts DH, van der Klei IJ. Moonlighting proteins: an intriguing mode of multitasking. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803:520–525. - PubMed
-
- Hult K, Berglund P. Enzyme promiscuity: mechanism and applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2007;25:231–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

