Analysis of her1 and her7 mutants reveals a spatio temporal separation of the somite clock module
- PMID: 22723933
- PMCID: PMC3377618
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039073
Analysis of her1 and her7 mutants reveals a spatio temporal separation of the somite clock module
Abstract
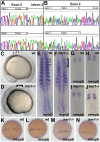
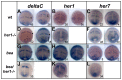
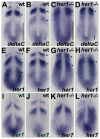
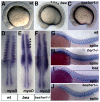
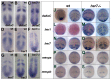
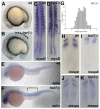
Somitogenesis is controlled by a genetic network consisting of an oscillator (clock) and a gradient (wavefront). The "hairy and Enhancer of Split"- related (her) genes act downstream of the Delta/Notch (D/N) signaling pathway, and are crucial components of the segmentation clock. Due to genome duplication events, the zebrafish genome, possesses two gene copies of the mouse Hes7 homologue: her1 and her7. To better understand the functional consequences of this gene duplication, and to determine possible independent roles for these two genes during segmentation, two zebrafish mutants her1(hu2124) and her7(hu2526) were analyzed. In the course of embryonic development, her1(hu2124) mutants exhibit disruption of the three anterior-most somite borders, whereas her7(hu2526) mutants display somite border defects restricted to somites 8 (+/-3) to 17 (+/-3) along the anterior-posterior axis. Analysis of the molecular defects in her1(hu2124) mutants reveals a her1 auto regulatory feedback loop during early somitogenesis that is crucial for correct patterning and independent of her7 oscillation. This feedback loop appears to be restricted to early segmentation, as cyclic her1 expression is restored in her1(hu2124) embryos at later stages of development. Moreover, only the anterior deltaC expression pattern is disrupted in the presomitic mesoderm of her1(hu2124) mutants, while the posterior expression pattern of deltaC remains unaltered. Together, this data indicates the existence of an independent and genetically separable anterior and posterior deltaC clock modules in the presomitic mesdorm (PSM).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Palmeirim I, Henrique D, Ish-Horowicz D, Pourquie O. Avian hairy gene expression identifies a molecular clock linked to vertebrate segmentation and somitogenesis. Cell. 1997;91:639–648. - PubMed
-
- Jouve C, Palmeirim I, Henrique D, Beckers J, Gossler A, et al. Notch signalling is required for cyclic expression of the hairy-like gene HES1 in the presomitic mesoderm. Development. 2000;127:1421–1429. - PubMed
-
- Bessho Y, Kageyama R. Oscillations, clocks and segmentation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003;13:379–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

