Evaluation of 3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazole as a novel anti-inflammatory drug candidate
- PMID: 22723938
- PMCID: PMC3377599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039104
Evaluation of 3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazole as a novel anti-inflammatory drug candidate
Abstract
Background: 3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazole (DIC) is a five-membered heterocyclic compound containing a N-O bond. The anti-inflammatory effects of this compound were studied both in vitro and in vivo.
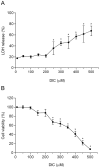
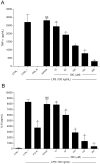
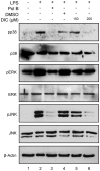
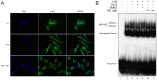
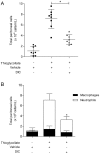
Principal findings: DIC effectively decreased TNF-α and IL-6 release from LPS-stimulated macrophages in a dose dependent manner. DIC diminished the levels of COX-2 with subsequent inhibition of PGE(2) production. DIC also compromised HMGB1 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Moreover, DIC prevented the nuclear translocation of NF-κB and inhibited the MAPK pathway. In vivo, DIC inhibited migration of neutrophils to the peritoneal cavity of mice.
Conclusions: This study presents the potential utilization of a synthetic compound, as a lead for the development of novel anti-inflammatory drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ketamine inhibits LPS-induced HGMB1 release in vitro and in vivo.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Nov;23(1):14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25133650
-
Isoliquiritigenin isolated from the roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis inhibits LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via the attenuation of NF-kappaB in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 14;584(1):175-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.032. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18295200
-
The p38 MAPK inhibitor JLU1124 inhibits the inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide through the MAPK-NF-κB pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Nov;17(3):785-92. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24070708
-
The inhibition of JNK MAPK and NF-κB signaling by tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages is associated with its anti-inflammatory effect.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):267-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.026. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24076326
-
Imperatorin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-κB and MAPKs activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Inflammation. 2012 Dec;35(6):1764-72. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9495-9. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22890309
Cited by
-
HMGB1 in health and disease.Mol Aspects Med. 2014 Dec;40:1-116. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Mol Aspects Med. 2014. PMID: 25010388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of HMGB1 in the Pathogenesis of Schistosomiasis Liver Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 12;9:1979. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01979. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30258438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:907–916. - PubMed
-
- Wagner G, Laufer S. Small molecular anti-cytokine agents. Med Res Rev. 2006;26:1–62. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC. p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:717–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

