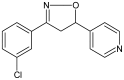
Evaluation of 3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazole as a novel anti-inflammatory drug candidate
- PMID: 22723938
- PMCID: PMC3377599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039104
Evaluation of 3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazole as a novel anti-inflammatory drug candidate
Abstract
Background: 3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazole (DIC) is a five-membered heterocyclic compound containing a N-O bond. The anti-inflammatory effects of this compound were studied both in vitro and in vivo.
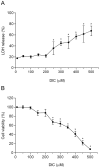
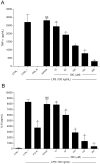
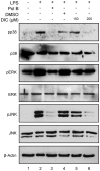
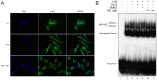
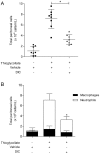
Principal findings: DIC effectively decreased TNF-α and IL-6 release from LPS-stimulated macrophages in a dose dependent manner. DIC diminished the levels of COX-2 with subsequent inhibition of PGE(2) production. DIC also compromised HMGB1 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Moreover, DIC prevented the nuclear translocation of NF-κB and inhibited the MAPK pathway. In vivo, DIC inhibited migration of neutrophils to the peritoneal cavity of mice.
Conclusions: This study presents the potential utilization of a synthetic compound, as a lead for the development of novel anti-inflammatory drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:907–916. - PubMed
-
- Wagner G, Laufer S. Small molecular anti-cytokine agents. Med Res Rev. 2006;26:1–62. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC. p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:717–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

