Inhibition of apoptosis blocks human motor neuron cell death in a stem cell model of spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 22723941
- PMCID: PMC3378532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039113
Inhibition of apoptosis blocks human motor neuron cell death in a stem cell model of spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
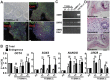
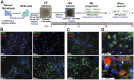
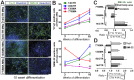
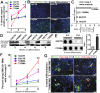
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a genetic disorder caused by a deletion of the survival motor neuron 1 gene leading to motor neuron loss, muscle atrophy, paralysis, and death. We show here that induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines generated from two Type I SMA subjects-one produced with lentiviral constructs and the second using a virus-free plasmid-based approach-recapitulate the disease phenotype and generate significantly fewer motor neurons at later developmental time periods in culture compared to two separate control subject iPSC lines. During motor neuron development, both SMA lines showed an increase in Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis and increased caspase-8 and-3 activation. Importantly, this could be mitigated by addition of either a Fas blocking antibody or a caspase-3 inhibitor. Together, these data further validate this human stem cell model of SMA, suggesting that specific inhibitors of apoptotic pathways may be beneficial for patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
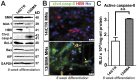
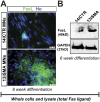
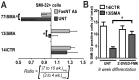
References
-
- Lefebvre S, Burlet P, Liu Q, Bertrandy S, Clermont O, et al. Correlation between severity and SMN protein level in spinal muscular atrophy. Nat Genet. 1997;16:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Burghes AH, Ingraham SE, Kote-Jarai Z, Rosenfeld S, Herta N, et al. Linkage mapping of the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Hum Genet. 1994;93:305–312. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Frezal J, Munnich A, Melki J. The role of the SMN gene in proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1531–1536. - PubMed
-
- Jablonka S, Rossoll W, Schrank B, Sendtner M. The role of SMN in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol. 2000;247:I37–I42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

