Novel olanzapine analogues presenting a reduced H1 receptor affinity and retained 5HT2A/D2 binding affinity ratio
- PMID: 22726212
- PMCID: PMC3485633
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-12-8
Novel olanzapine analogues presenting a reduced H1 receptor affinity and retained 5HT2A/D2 binding affinity ratio
Abstract
Background: Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic drug with high clinical efficacy, but which can cause severe weight gain and metabolic disorders in treated patients. Blockade of the histamine 1 (H1) receptors is believed to play a crucial role in olanzapine induced weight gain, whereas the therapeutic effects of this drug are mainly attributed to its favourable serotoninergic 2A and dopamine 2 (5HT2A/D2) receptor binding affinity ratios.
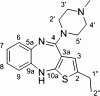
Results: We have synthesized novel olanzapine analogues 8a and 8b together with the already known derivative 8c and we have examined their respective in vitro affinities for the 5HT2A, D2, and H1 receptors.
Conclusions: We suggest that thienobenzodiazepines 8b and 8c with lower binding affinity for the H1 receptors, but similar 5HT2A/D2 receptor binding affinity ratios to those of olanzapine. These compounds may offer a better pharmacological profile than olanzapine for treating patients with schizophrenia.
Figures




References
-
- American Diabetes Association, American Psychiatric Association, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologist. Consensus development conference on antipsychotic drugs and obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:596–601. - PubMed
-
- Worrel JA, Marken PA, Beckman SE, Ruehter VL. Atypical antipsychotic agents: a critical review. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2000;57:238–255. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

