Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota
- PMID: 22726443
- PMCID: PMC3442780
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.037
Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota
Abstract
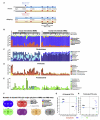
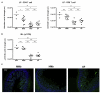
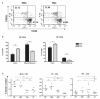
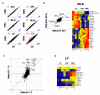
Gut microbial induction of host immune maturation exemplifies host-microbe mutualism. We colonized germ-free (GF) mice with mouse microbiota (MMb) or human microbiota (HMb) to determine whether small intestinal immune maturation depends on a coevolved host-specific microbiota. Gut bacterial numbers and phylum abundance were similar in MMb and HMb mice, but bacterial species differed, especially the Firmicutes. HMb mouse intestines had low levels of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells, few proliferating T cells, few dendritic cells, and low antimicrobial peptide expression--all characteristics of GF mice. Rat microbiota also failed to fully expand intestinal T cell numbers in mice. Colonizing GF or HMb mice with mouse-segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB) partially restored T cell numbers, suggesting that SFB and other MMb organisms are required for full immune maturation in mice. Importantly, MMb conferred better protection against Salmonella infection than HMb. A host-specific microbiota appears to be critical for a healthy immune system.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Host and microbes date exclusively.Cell. 2012 Jun 22;149(7):1428-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.005. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22726431
-
Mucosal immunology: Any old bugs won't do.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Jul 25;12(8):554-5. doi: 10.1038/nri3270. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22828909 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chassin C, Kocur M, Pott J, Duerr CU, Gütle D, Lotz M, Hornef MW. miR-146a mediates protective innate immune tolerance in the neonate intestine. Cell Host Microbe. 2010;8:358–368. - PubMed
-
- Chung H, Kasper DL. Microbiota-stimulated immune mechanisms to maintain gut homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010;22:455–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

