Resistin-like molecule α1 (Fizz1) recruits lung dendritic cells without causing pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 22726462
- PMCID: PMC3485088
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-51
Resistin-like molecule α1 (Fizz1) recruits lung dendritic cells without causing pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Resistin-like molecule alpha or found in inflammatory zone protein (Fizz1) is increased in pulmonary epithelial cells and also in limited amounts by other lung cells during various lung injuries and fibrosis. However, the direct role of Fizz1 produced in the pulmonary epithelium has not been determined.
Methods: Fizz1 Transgenic mice (CCSP/Fizz1) were generated that overexpress Fizz1 in the lung epithelium under the control of a doxycycline (Dox) inducible lung epithelial cell specific promoter Scgb1a1 (Clara cell secretory protein, CCSP). Histology and FACS analysis of lung cells were used to identify the direct effects of Fizz1 in the transgenic mice (Dox treated) when compared with control (CCSP/-) mice. Intratracheal bleomycin sulfate or silica in saline and saline alone were used to study the role of Fizz1 during bleomycin- and silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in CCSP/Fizz1 and CCSP/- mice. Weight change, pulmonary inflammation, and fibrosis were assessed 10 days post bleomycin or 28 days post silica challenge.
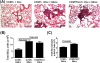
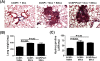
Results: When CCSP/Fizz1 mice were fed Dox food, elevated Fizz1 protein was detected in lung homogenates by western blot. Lungs of mice in which Fizz1 was induced in the epithelium contained increased lung cells staining for CD11c and F4/80 by FACS analysis consistent with increased dendritic cells however, no changes were observed in the percentage of interstitial macrophages compared to CCSP/- controls. No significant changes were found in the lung histology of CCSP/Fizz1 mice after up to 8 weeks of overexpression compared to CCSP/- controls. Overexpression of Fizz1 prior to challenge or following challenge with bleomycin or silica did not significantly alter airway inflammation or fibrosis compared to control mice.
Conclusions: The current study demonstrates that epithelial cell derived Fizz1 is sufficient to increase the bone-marrow derived dendritic cells in the lungs, but it is not sufficient to cause lung fibrosis or alter chemical or particle-induced fibrosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The in vivo fibrotic role of FIZZ1 in pulmonary fibrosis.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 6;9(2):e88362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088362. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24516640 Free PMC article.
-
Alternaria induces STAT6-dependent acute airway eosinophilia and epithelial FIZZ1 expression that promotes airway fibrosis and epithelial thickness.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 15;188(6):2622-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101632. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22327070 Free PMC article.
-
In situ evidence of collagen V and signaling pathway of found inflammatory zone 1 (FIZZ1) is associated with silicotic granuloma in lung mice.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Sep;216(9):153094. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153094. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32825961
-
Use of human amniotic epithelial cells in mouse models of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2018 May 17;13(5):e0197658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197658. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29772024 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary phenotype of CCSP/UG deficient mice: a consequence of CCSP deficiency or altered Clara cell function?Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;923:202-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05531.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193758 Review.
Cited by
-
Allergen-induced resistin-like molecule-α promotes esophageal epithelial cell hyperplasia in eosinophilic esophagitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Sep 1;307(5):G499-507. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00141.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24994859 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal phenotypic features distinguish polarized macrophages in vitro.Autoimmunity. 2015 May;48(3):161-76. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1027816. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Autoimmunity. 2015. PMID: 25826285 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary osteoclast-like cells in silica induced pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Adv. 2024 Jul 12;10(28):eadl4913. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl4913. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38985878 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the αvβ6 integrin leads to limited alteration of TGF-α-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Apr 15;306(8):L726-35. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00357.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24508732 Free PMC article.
-
Retnla overexpression attenuates allergic inflammation of the airway.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 21;9(11):e112666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112666. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25415454 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

