Dual leucine zipper kinase is required for retrograde injury signaling and axonal regeneration
- PMID: 22726832
- PMCID: PMC3383631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.028
Dual leucine zipper kinase is required for retrograde injury signaling and axonal regeneration
Abstract
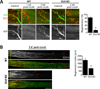
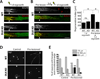
Here we demonstrate that the dual leucine zipper kinase (DLK) promotes robust regeneration of peripheral axons after nerve injury in mice. Peripheral axon regeneration is accelerated by prior injury; however, DLK KO neurons do not respond to a preconditioning lesion with enhanced regeneration in vivo or in vitro. Assays for activation of transcription factors in injury-induced proregenerative pathways reveal that loss of DLK abolishes upregulation of p-STAT3 and p-cJun in the cell body after axonal injury. DLK is not required for the phosphorylation of STAT3 at the site of nerve injury but is necessary for retrograde transport of p-STAT3 to the cell body. These data demonstrate that DLK enhances regeneration by promoting a retrograde injury signal that is required for the activation of the neuronal proregenerative program.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
DLK: the "preconditioning" signal for axon regeneration?Neuron. 2012 Jun 21;74(6):961-3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.005. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22726825
References
-
- Bareyre FM, Garzorz N, Lang C, Misgeld T, Buning H, Kerschensteiner M. In vivo imaging reveals a phase-specific role of STAT3 during central and peripheral nervous system axon regeneration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108:6282–6287. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG13730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS060709/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS065053/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE022000/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- NS070053/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065053/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060709/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS065053/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS070053/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

