Neuroendocrine influences on cancer progression
- PMID: 22728325
- PMCID: PMC3467346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.06.005
Neuroendocrine influences on cancer progression
Abstract
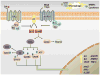
During the past decade, new studies have continued to shed light on the role of neuroendocrine regulation of downstream physiological and biological pathways relevant to cancer growth and progression. More specifically, our knowledge of the effects of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) on cancer biology has been greatly expanded by new data demonstrating how the cellular immune response, inflammatory processes, tumor-associated angiogenesis, and tumor cell invasion and survival converge to promote tumor growth. This review will summarize these studies, while synthesizing clinical, cellular and molecular research that has continued to unearth the biological events mediating the interplay between SNS-related processes and cancer progression.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aguado LI, Ojeda SR. Prepubertal ovarian function is finely regulated by direct adrenergic influences. Role of noradrenergic innervation. Endocrinology. 1984;114:1845–1853. - PubMed
-
- Algazi M, Plu-Bureau G, Flahault A, Dondon MG, Le MG. Could treatments with beta-blockers be associated with a reduction in cancer risk? Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2004;52:53–65. - PubMed
-
- Andersen BL, Thornton LM, Shapiro CL, Farrar WB, Mundy BL, Yang HC, Carson WE., 3rd Biobehavioral, immune, and health benefits following recurrence for psychological intervention participants. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2010;16:3270–3278. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA109298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104825/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA083639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- (P50CA083639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA110793/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA151668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA110793/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA104825/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

