Calculation of the stabilization energies of oxidatively damaged guanine base pairs with guanine
- PMID: 22728364
- PMCID: PMC6268328
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17066705
Calculation of the stabilization energies of oxidatively damaged guanine base pairs with guanine
Abstract
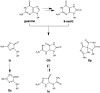
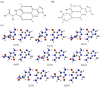
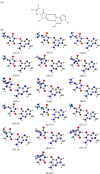
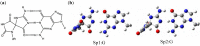
DNA is constantly exposed to endogenous and exogenous oxidative stresses. Damaged DNA can cause mutations, which may increase the risk of developing cancer and other diseases. G:C-C:G transversions are caused by various oxidative stresses. 2,2,4-Triamino-5(2H)-oxazolone (Oz), guanidinohydantoin (Gh)/iminoallantoin (Ia) and spiro-imino-dihydantoin (Sp) are known products of oxidative guanine damage. These damaged bases can base pair with guanine and cause G:C-C:G transversions. In this study, the stabilization energies of these bases paired with guanine were calculated in vacuo and in water. The calculated stabilization energies of the Ia:G base pairs were similar to that of the native C:G base pair, and both bases pairs have three hydrogen bonds. By contrast, the calculated stabilization energies of Gh:G, which form two hydrogen bonds, were lower than the Ia:G base pairs, suggesting that the stabilization energy depends on the number of hydrogen bonds. In addition, the Sp:G base pairs were less stable than the Ia:G base pairs. Furthermore, calculations showed that the Oz:G base pairs were less stable than the Ia:G, Gh:G and Sp:G base pairs, even though experimental results showed that incorporation of guanine opposite Oz is more efficient than that opposite Gh/Ia and Sp.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Products of Oxidative Guanine Damage Form Base Pairs with Guanine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;21(20):7645. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207645. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33076559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calculating distortions of short DNA duplexes with base pairing between an oxidatively damaged guanine and a guanine.Molecules. 2014 Jul 28;19(8):11030-44. doi: 10.3390/molecules190811030. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25072203 Free PMC article.
-
The R- and S-diastereoisomeric effects on the guanidinohydantoin-induced mutations in DNA.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015 Jul 21;17(27):18111-20. doi: 10.1039/c5cp02636a. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 26099851
-
Generation, repair and replication of guanine oxidation products.Genes Environ. 2017 Aug 1;39:21. doi: 10.1186/s41021-017-0081-0. eCollection 2017. Genes Environ. 2017. PMID: 28781714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible cause of G-C-->C-G transversion mutation by guanine oxidation product, imidazolone.Chem Biol. 2001 Apr;8(4):369-78. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(01)00019-9. Chem Biol. 2001. PMID: 11325592
Cited by
-
Contiguous 2,2,4-triamino-5(2H)-oxazolone obstructs DNA synthesis by DNA polymerases α, β, η, ι, κ, REV1 and Klenow Fragment exo-, but not by DNA polymerase ζ.J Biochem. 2016 Mar;159(3):323-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvv103. Epub 2015 Oct 21. J Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26491064 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of guanine oxidation products in double-stranded DNA and proposed guanine oxidation pathways in single-stranded, double-stranded or quadruplex DNA.Biomolecules. 2014 Feb 10;4(1):140-59. doi: 10.3390/biom4010140. Biomolecules. 2014. PMID: 24970209 Free PMC article.
-
Products of Oxidative Guanine Damage Form Base Pairs with Guanine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;21(20):7645. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207645. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33076559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of stability of base pairs containing an oxazolone on DNA elongation.J Nucleic Acids. 2014;2014:178350. doi: 10.1155/2014/178350. Epub 2014 Dec 7. J Nucleic Acids. 2014. PMID: 25574383 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of base substitution mutagenesis in cancer genomes.Genes (Basel). 2014 Mar 5;5(1):108-46. doi: 10.3390/genes5010108. Genes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24705290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shibutani S., Takeshita M., Grollman A.P. Insertion of specific bases during DNA synthesis past the oxidation-damaged base 8-oxodG. Nature. 1991;349:431–434. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J., Berger M., Buchko G.W., Joshi P.C., Raoul S., Ravanat J.-L. 2,2-Diamino-4-[(3,5-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)amino]-5-(2H)-oxazolone: A novel and predominant radical oxidation product of 3',5'-di-O-acetyl-2'-deoxyguanosine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116:7403–7404.
-
- Kino K., Saito I., Sugiyama H. Product analysis of GG-specific photooxidation of DNA via electron transfer: 2-Aminoimidazolone as a major guanine oxidation product. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120:7373–7374. doi: 10.1021/ja980763a. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

