Free hemoglobin induction of pulmonary vascular disease: evidence for an inflammatory mechanism
- PMID: 22728465
- PMCID: PMC3423829
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00074.2012
Free hemoglobin induction of pulmonary vascular disease: evidence for an inflammatory mechanism
Abstract
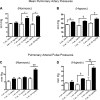
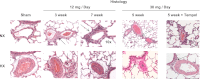
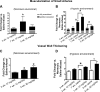
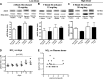
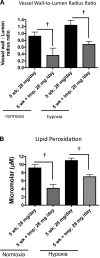
Cell-free hemoglobin (Hb) exposure may be a pathogenic mediator in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), and when combined with chronic hypoxia the potential for exacerbation of PAH and vascular remodeling is likely more pronounced. We hypothesized that Hb may contribute to hypoxia-driven PAH collectively as a prooxidant, inflammatory, and nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. Using programmable micropump technology, we exposed male Sprague-Dawley rats housed under room air or hypoxia to 12 or 30 mg per day Hb for 3, 5, and 7 wk. Blood pressure, cardiac output, right ventricular hypertrophy, and indexes of pulmonary vascular remodeling were evaluated. Additionally, markers of oxidative stress, NO bioavailability and inflammation were determined. Hb increased pulmonary arterial (PA) pressure, pulmonary vessel wall stiffening, and right heart hypertrophy with temporal and dose dependence in both room air and hypoxic cohorts. Hb induced a modest increase in plasma oxidative stress markers (malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal), no change in NO bioavailability, and increased lung ICAM protein expression. Treatment with the antioxidant Tempol attenuated Hb-induced pulmonary arterial wall thickening, but not PA pressures or ICAM expression. Chronic exposure to low plasma Hb concentrations (range = 3-10 μM) lasting up to 7 wk in rodents induces pulmonary vascular disease via inflammation and to a lesser extent by Hb-mediated oxidation. Tempol demonstrated a modest effect on the attenuation of Hb-induced pulmonary vascular disease. NO bioavailability was found to be of minimal importance in this model.
Figures






References
-
- Buehler P, D'Agnillo F. Toxicological consequences of extracellular hemoglobin: biochemical and physiological perspectives. Antioxid Redox Signal 12: 275–291, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bunn HF, Nathan DG, Dover GJ, Hebbel RP, Platt OS, Rosse WF, Ware RE. Pulmonary hypertension and nitric oxide depletion in sickle cell disease. Blood 116: 687–692, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee PK, Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Zacharowski K, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, Thiemermann C. Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces oxidant stress-mediated renal dysfunction and injury in the rat. Kidney Int 58: 658–673, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Christou H, Morita T, Hsieh CM, Koike H, Arkonac B, Perrella MA, Kourembanas S. Prevention of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by enhancement of endogenous heme oxygenase-1 in the rat. Circ Res 86: 1224–1229, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

