Tubulin nucleotide status controls Sas-4-dependent pericentriolar material recruitment
- PMID: 22729084
- PMCID: PMC3411905
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2527
Tubulin nucleotide status controls Sas-4-dependent pericentriolar material recruitment
Abstract
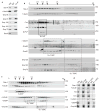
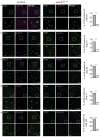
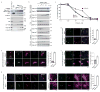
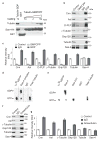
Regulated centrosome biogenesis is required for accurate cell division and for maintaining genome integrity. Centrosomes consist of a centriole pair surrounded by a protein network known as pericentriolar material (PCM). PCM assembly is a tightly regulated, critical step that determines the size and capability of centrosomes. Here, we report a role for tubulin in regulating PCM recruitment through the conserved centrosomal protein Sas-4. Tubulin directly binds to Sas-4; together they are components of cytoplasmic complexes of centrosomal proteins. A Sas-4 mutant, which cannot bind tubulin, enhances centrosomal protein complex formation and has abnormally large centrosomes with excessive activity. These results suggest that tubulin negatively regulates PCM recruitment. Whereas tubulin-GTP prevents Sas-4 from forming protein complexes, tubulin-GDP promotes it. Thus, the regulation of PCM recruitment by tubulin depends on its GTP/GDP-bound state. These results identify a role for tubulin in regulating PCM recruitment independent of its well-known role as a building block of microtubules. On the basis of its guanine-bound state, tubulin can act as a molecular switch in PCM recruitment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Nigg EA, Raff JW. Centrioles, centrosomes, and cilia in health and disease. Cell. 2009;139:663–678. - PubMed
-
- Conduit PT, et al. Centrioles regulate centrosome size by controlling the rate of Cnn incorporation into the PCM. Curr Biol. 2010;20:2178–2186. - PubMed
-
- Kirkham M, Muller-Reichert T, Oegema K, Grill S, Hyman AA. SAS-4 is a C. elegans centriolar protein that controls centrosome size. Cell. 2003;112:575–587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

