Mutagenesis of the residues forming an ion binding pocket of the NtpK subunit of Enterococcus hirae V-ATPase
- PMID: 22730119
- PMCID: PMC3415527
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00714-12
Mutagenesis of the residues forming an ion binding pocket of the NtpK subunit of Enterococcus hirae V-ATPase
Abstract
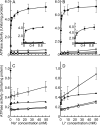
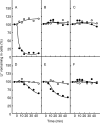
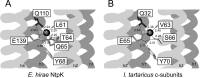
The crystal structures of the Na(+)- and Li(+)-bound NtpK rings of Enterococcus hirae V-ATPase have been obtained. The coupling ion (Na(+) or Li(+)) was surrounded by five oxygen atoms contributed by residues T64, Q65, Q110, E139, and L61, and the hydrogen bonds of the side chains of Q110, Y68, and T64 stabilized the position of the E139 γ carboxylate essential for ion occlusion (PDB accession numbers 2BL2 and 2CYD). We previously indicated that an NtpK mutant strain (E139D) lost tolerance to sodium but not to lithium at alkaline pHs and suggested that the E139 residue is indispensable for the enzymatic activity of E. hirae V-ATPase linked with the sodium tolerance of this bacterium. In this study, we examined the activities of V-ATPase in which these four residues, except for E139, were substituted. The V-ATPase activities of the Q65A and Y68A mutants were slightly retained, but those of the T64A and Q110A mutants were negligible. Among the residues, T64 and Q110 are indispensable for the ion coupling of E. hirae V-ATPase, in addition to the essential residue E139.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of the glutamate-139 residue of the V-type Na+-ATPase NtpK subunit in catalytic turnover linked with salt tolerance of Enterococcus hirae.J Bacteriol. 2011 Jul;193(14):3657-61. doi: 10.1128/JB.01537-10. Epub 2011 May 20. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21602356 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine residue at position 573 in Enterococcus hirae vacuolar-type ATPase NtpI subunit plays a crucial role in Na+ translocation.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 5;277(27):24405-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200973200. Epub 2002 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11983695
-
Structure of the rotor ring modified with N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide of the Na+-transporting vacuolar ATPase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 16;108(33):13474-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103287108. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21813759 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and mechanism of vacuolar Na+-translocating ATPase from Enterococcus hirae.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2005 Dec;37(6):411-3. doi: 10.1007/s10863-005-9481-0. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2005. PMID: 16691474 Review.
-
Infrared spectroscopic studies on the V-ATPase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1847(1):134-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.07.020. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25111748 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and Genomic Properties of Chitinispirillum alkaliphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., A Haloalkaliphilic Anaerobic Chitinolytic Bacterium Representing a Novel Class in the Phylum Fibrobacteres.Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 31;7:407. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00407. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27065971 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Highly Alkaline-Resistant Carnobacterium maltaromaticum V-Type ATPase from the Dairy Product Based on Comparative Genomics.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 6;9(6):1233. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061233. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34204143 Free PMC article.
-
Six states of Enterococcus hirae V-type ATPase reveals non-uniform rotor rotation during turnover.Commun Biol. 2023 Jul 28;6(1):755. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05110-8. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37507515 Free PMC article.
-
Prokaryotic Life Associated with Coal-Fire Gas Vents Revealed by Metagenomics.Biology (Basel). 2023 May 15;12(5):723. doi: 10.3390/biology12050723. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams A, Jensen C. 1984. Altered expression of the H+ ATPase in Streptococcus faecalis membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 122:151–157 - PubMed
-
- Boyer PD. 1993. The binding change mechanism for ATP synthase—some probabilities and possibilities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1140:215–250 - PubMed
-
- Fillingame RH, Jiang W, Dmitriev OY. 2000. Coupling H+ transport to rotary catalysis in F-type ATP synthases: structure and organization of the transmembrane rotary motor. J. Exp. Biol. 203:9–17 - PubMed
-
- Hosaka T, Takase K, Murata T, Kakinuma Y, Yamato I. 2006. Deletion analysis of the subunit genes of V-type Na+-ATPase from Enterococcus hirae. J. Biochem. 139:1045–1052 - PubMed
-
- Kaim G, Wehrle F, Gerike U, Dimroth P. 1997. Molecular basis for the coupling ion selectivity of F1F0 ATP synthases: probing the liganding groups for Na+ and Li+ in the c subunit of the ATP synthase from Propionigenium modestum. Biochemistry 36:9185–9194 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

