Identification of compounds with anti-convulsant properties in a zebrafish model of epileptic seizures
- PMID: 22730455
- PMCID: PMC3484860
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.010090
Identification of compounds with anti-convulsant properties in a zebrafish model of epileptic seizures
Abstract
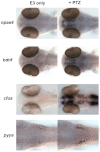
The availability of animal models of epileptic seizures provides opportunities to identify novel anticonvulsants for the treatment of people with epilepsy. We found that exposure of 2-day-old zebrafish embryos to the convulsant agent pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) rapidly induces the expression of synaptic-activity-regulated genes in the CNS, and elicited vigorous episodes of calcium (Ca(2+)) flux in muscle cells as well as intense locomotor activity. We then screened a library of ∼2000 known bioactive small molecules and identified 46 compounds that suppressed PTZ-inducedtranscription of the synaptic-activity-regulated gene fos in 2-day-old (2 dpf) zebrafish embryos. Further analysis of a subset of these compounds, which included compounds with known and newly identified anticonvulsant properties, revealed that they exhibited concentration-dependent inhibition of both locomotor activity and PTZ-induced fos transcription, confirming their anticonvulsant characteristics. We conclude that this in situ hybridisation assay for fos transcription in the zebrafish embryonic CNS is a robust, high-throughput in vivo indicator of the neural response to convulsant treatment and lends itself well to chemical screening applications. Moreover, our results demonstrate that suppression of PTZ-induced fos expression provides a sensitive means of identifying compounds with anticonvulsant activities.
Figures





References
-
- Anandahan A., Tamilselvan K., Radhiga T., Rao S., Essa M. M., Manivasagam T. (2012). Theaflavin, a black tea polyphenol, protects nigral dopaminergic neurons against chronic MPTP/probenecid induced Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 1433, 104–113 - PubMed
-
- Baraban S. C., Taylor M. R., Castro P. A., Baier H. (2005). Pentylenetetrazole induced changes in zebrafish behavior, neural activity and c-fos expression. Neuroscience 131, 759–768 - PubMed
-
- Berghmans S., Hunt J., Roach A., Goldsmith P. (2007). Zebrafish offer the potential for a primary screen to identify a wide range of potential anticonvulsants. Epilepsy Res. 75, 18–28 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

