RBFOX1 regulates both splicing and transcriptional networks in human neuronal development
- PMID: 22730494
- PMCID: PMC3441119
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/dds240
RBFOX1 regulates both splicing and transcriptional networks in human neuronal development
Abstract
RNA splicing plays a critical role in the programming of neuronal differentiation and, consequently, normal human neurodevelopment, and its disruption may underlie neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. The RNA-binding protein, fox-1 homolog (RBFOX1; also termed A2BP1 or FOX1), is a neuron-specific splicing factor predicted to regulate neuronal splicing networks clinically implicated in neurodevelopmental disease, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but only a few targets have been experimentally identified. We used RNA sequencing to identify the RBFOX1 splicing network at a genome-wide level in primary human neural stem cells during differentiation. We observe that RBFOX1 regulates a wide range of alternative splicing events implicated in neuronal development and maturation, including transcription factors, other splicing factors and synaptic proteins. Downstream alterations in gene expression define an additional transcriptional network regulated by RBFOX1 involved in neurodevelopmental pathways remarkably parallel to those affected by splicing. Several of these differentially expressed genes are further implicated in ASD and related neurodevelopmental diseases. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis demonstrates a high degree of connectivity among these disease-related genes, highlighting RBFOX1 as a key factor coordinating the regulation of both neurodevelopmentally important alternative splicing events and clinically relevant neuronal transcriptional programs in the development of human neurons.
Figures
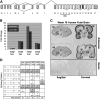
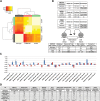
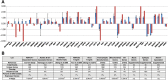
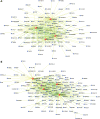
References
-
- Blencowe B.J., Ahmad S., Lee L.J. Current-generation high-throughput sequencing: deepening insights into mammalian transcriptomes. Genes Dev. 2009;23:1379–1386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH074362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH081754/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30HD004612/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH090238/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081754/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08MH074362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH086297/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08MH86297/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00MH090238/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

