Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 22731712
- PMCID: PMC3384703
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06538.x
Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases
Abstract
Recent studies indicate that besides digestion and absorption of nutrients and water and electrolytes homeostasis, another key function of the intestine is to regulate the trafficking of environmental antigens across the host mucosal barrier. Intestinal tight junctions (TJs) create gradients for the optimal absorption and transport of nutrients and control the balance between tolerance and immunity to nonself antigens. To meet diverse physiological challenges, intestinal epithelial TJs must be modified rapidly and in a coordinated fashion by regulatory systems that orchestrate the state of assembly of the TJ multiprotein network. While considerable knowledge exists about TJ ultrastructure, relatively little is known about their physiological and pathophysiological regulation. Our discovery of zonulin, the only known physiologic modulator of intercellular TJs described so far, has increased our understanding of the intricate mechanisms that regulate the intestinal epithelial paracellular pathway and has led us to appreciate that its upregulation in genetically susceptible individuals leads to autoimmune diseases.
© 2012 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures
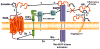
References
-
- Progress in Autoimmune Diseases Research. Report to Congress, National Institutes of Health, The Autoimmune Diseases Coordinating Committee; March 2005.
-
- National Institutes of Health. Plan. 2002. Autoimmune Diseases research.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

