Challenges and opportunities in the targeting of fibroblast growth factor receptors in breast cancer
- PMID: 22731805
- PMCID: PMC3446326
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3139
Challenges and opportunities in the targeting of fibroblast growth factor receptors in breast cancer
Abstract
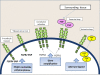
Activation of the fibroblast growth factor receptor pathway is a common event in many cancer types. Here we review the role of fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling in breast cancer, from SNPs in FGFR2 that influence breast cancer risk and SNPs in FGFR4 that associate with breast cancer prognosis, and potential therapeutic targets such as receptor amplification and aberrant autocrine and paracrine ligand expression. We discuss the multiple therapeutic strategies in preclinical and clinical development and the current and future challenges to successfully targeting this pathway in cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Osborne CK, Neven P, Dirix LY, Mackey JR, Robert J, Underhill C, Schiff R, Gutierrez C, Migliaccio I, Anagnostou VK, Rimm DL, Magill P, Sellers M. Gefitinib or placebo in combination with tamoxifen in patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a randomized phase II study. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:1147–1159. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1869. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Cosimo S, Bendell JC, Cervantes-Ruiperez A, Roda D, Prudkin L, Stein MN, Leighton-Swayze A, Song Y, Ebbinghaus S, Baselga J. A phase I study of the oral mTOR inhibitor ridaforolimus (RIDA) in combination with the IGF-1R antibody dalotozumab (DALO) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors [abstract 3008] J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(Suppl):15s..
-
- De Moerlooze L, Spencer-Dene B, Revest JM, Hajihosseini M, Rosewell I, Dickson C. An important role for the IIIb isoform of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) in mesenchymal-epithelial signalling during mouse organogenesis. Development. 2000;127:483–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

