Lactoferrin regulates an axis involving CD11b and CD49d integrins and the chemokines MIP-1α and MCP-1 in GM-CSF-treated human primary eosinophils
- PMID: 22731992
- PMCID: PMC3464068
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2011.0111
Lactoferrin regulates an axis involving CD11b and CD49d integrins and the chemokines MIP-1α and MCP-1 in GM-CSF-treated human primary eosinophils
Abstract
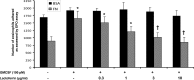
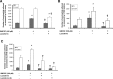
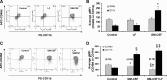
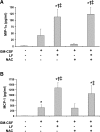
Eosinophils are multifunctional immune cells that contribute to innate and adaptive immune/repair responses. Lactoferrin (LF) is an iron-binding protein indicated to alter cell adhesion and immune function by receptor-mediated interactions or by participating in redox mechanisms. The eosinophil adhesion molecules, αMβ2 and α4β1, are differentially expressed following exposure to the cytokine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and various redox agents. We hypothesized that LF can alter the function and production of proteins involved in adhesion/migration. Utilizing eosinophil peroxidase activity or fluorescent labeling adhesion assays, LF reduced GM-CSF-induced eosinophil adhesion in the presence of fibronectin or vascular adhesion molecule-1 compared with GM-CSF treatment alone. Flow cytometric analysis of eosinophil αM (CD11b) and α4 (CD49d) integrins revealed that cotreatments (24 h) with LF plus GM-CSF induced a significant increase in CD11b compared with control and GM-CSF treatments but a significant decrease in CD49d compared with control and GM-CSF treatments. These changes in CD11b and CD49d levels were significantly correlated with the increased production of chemokines (macrophage inflammatory Protein-1α, monocyte chemotactic protein-1) and an identified increase in S100A9 production. Thus, LF release at sites of inflammation may alter eosinophil recruitment/activation and possibly the progression of diseases such as cancer and asthma where significant eosinophil influx has been described.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential engagement of modules 1 and 4 of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD106) by integrins alpha4beta1 (CD49d/29) and alphaMbeta2 (CD11b/18) of eosinophils.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 27;281(43):32175-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600943200. Epub 2006 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16943205
-
GM-CSF differentially regulates eosinophil and neutrophil adhesive interactions with vascular endothelium in vivo.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010 Dec;9(4):207-17. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21131700 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-gamma enhances human eosinophil effector functions induced by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor or interleukin-5.Immunol Lett. 2008 Jun 15;118(1):88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.03.005. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Immunol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18440651
-
The role of human mast cell-derived cytokines in eosinophil biology.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004 May;24(5):271-81. doi: 10.1089/107999004323065057. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004. PMID: 15153310 Review.
-
The effect of anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies on antigen-induced pulmonary inflammation in allergic rabbits.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2003;16(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/S1094-5539(03)00069-5. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12877819 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory effect of bovine lactoferrin during SARS-CoV-2 infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1456634. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456634. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483459 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GM-CSF in inflammatory diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;12(1):37-48. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.161. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26633290 Review.
-
Transitory presence of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in neonates is critical for control of inflammation.Nat Med. 2018 Feb;24(2):224-231. doi: 10.1038/nm.4467. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 29334374 Free PMC article.
-
Breast tumor and stromal cell responses to TGF-β and hypoxia in matrix deposition.Matrix Biol. 2013 Mar 11;32(2):95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2012.11.016. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Matrix Biol. 2013. PMID: 23262216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adhesion molecule cross-linking and cytokine exposure modulate IgE- and non-IgE-dependent basophil activation.Immunology. 2021 Jan;162(1):92-104. doi: 10.1111/imm.13268. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 32955733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas M. Lalive PH. Chofflon M. Simon HU. Chizzolini C. Ribi C. Hypereosinophilia in patients with multiple sclerosis treated with natalizumab. Neurology. 2011;77(16):1561–1564. - PubMed
-
- Adamko DJ. Wu Y. Ajamian F. Ilarraza R. Moqbel R. Gleich GJ. The effect of cationic charge on release of eosinophil mediators. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122(2):383–390. 390 e1–e4. - PubMed
-
- Adamko DJ. Wu Y. Gleich GJ. Lacy P. Moqbel R. The induction of eosinophil peroxidase release: improved methods of measurement and stimulation. J Immunol Methods. 2004;291(1–2):101–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

