Cholesterol metabolite, 5-cholesten-3β-25-diol-3-sulfate, promotes hepatic proliferation in mice
- PMID: 22732306
- PMCID: PMC3463675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.06.001
Cholesterol metabolite, 5-cholesten-3β-25-diol-3-sulfate, promotes hepatic proliferation in mice
Abstract
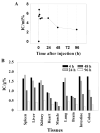
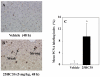
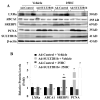
Oxysterols are well known as physiological ligands of liver X receptors (LXRs). Oxysterols, 25-hydroxycholesterol (25HC) and 27-hydroxycholesterol as endogenous ligands of LXRs, suppress cell proliferation via LXRs signaling pathway. Recent reports have shown that sulfated oxysterol, 5-cholesten-3β-25-diol-3-sulfate (25HC3S) as LXRs antagonist, plays an opposite direction to oxysterols in lipid biosynthesis. The present report was to explore the effect and mechanism of 25HC3S on hepatic proliferation in vivo. Following administration, 25HC3S had a 48 h half life in the circulation and widely distributed in mouse tissues. Profiler™ PCR array and RTqPCR analysis showed that either exogenous or endogenous 25HC3S generated by overexpression of oxysterol sulfotransferase (SULT2B1b) plus administration of 25HC significantly up-regulated the proliferation gene expression of Wt1, Pcna, cMyc, cyclin A, FoxM1b, and CDC25b in a dose-dependent manner in liver while substantially down-regulating the expression of cell cycle arrest gene Chek2 and apoptotic gene Apaf1. Either exogenous or endogenous administration of 25HC3S significantly induced hepatic DNA replication as measured by immunostaining of the PCNA labeling index and was associated with reduction in expression of LXR response genes, such as ABCA1 and SREBP-1c. Synthetic LXR agonist T0901317 effectively blocked 25HC3S-induced hepatic proliferation.
Conclusions: 25HC3S may be a potent regulator of hepatocyte proliferation and oxysterol sulfation may represent a novel regulatory pathway in liver proliferation via inactivating LXR signaling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


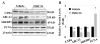
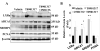
References
-
- O’Callaghan YC, Woods JA, O’Brien NM. Oxysterol-induced cell death in U937 and HepG2 cells at reduced and normal serum concentrations. Eur J Nutr. 1999;38:255–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

