Pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound increases penetration and therapeutic efficacy of monoclonal antibodies in murine xenograft tumors
- PMID: 22732476
- PMCID: PMC4219504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.06.025
Pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound increases penetration and therapeutic efficacy of monoclonal antibodies in murine xenograft tumors
Abstract
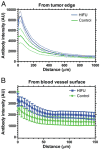
The success of radioimmunotherapy for solid tumors remains elusive due to poor biodistribution and insufficient tumor accumulation, in part, due to the unique tumor microenvironment resulting in heterogeneous tumor antibody distribution. Pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound (pulsed-HIFU) has previously been shown to increase the accumulation of (111)In labeled B3 antibody (recognizes Lewis(y) antigen). The objective of this study was to investigate the tumor penetration and therapeutic efficacy of pulsed-HIFU exposures combined with (90)Y labeled B3 mAb in an A431 solid tumor model. The ability of pulsed-HIFU (1 M Hz, spatial averaged temporal peak intensity=2685 W cm(-2); pulse repetition frequency=1 Hz; duty cycle=5%) to improve the tumor penetration and therapeutic efficacy of (90)Y labeled B3 mAb ((90)Y-B3) was evaluated in Le(y)-positive A431 tumors. Antibody penetration from the tumor surface and blood vessel surface was evaluated with fluorescently labeled B3, epi-fluorescent microscopy, and custom image analysis. Tumor size was monitored to determine treatment efficacy, indicated by survival, following various treatments with pulsed-HIFU and/or (90)Y-B3. The pulsed-HIFU exposures did not affect the vascular parameters including microvascular density, vascular size, and vascular architecture; although 1.6-fold more antibody was delivered to the solid tumors when combined with pulsed-HIFU. The distribution and penetration of the antibodies were significantly improved (p-value<0.05) when combined with pulsed-HIFU, only in the tumor periphery. Pretreatment with pulsed-HIFU significantly improved (p-value<0.05) survival over control treatments.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pulsed high-intensity focused ultrasound enhances uptake of radiolabeled monoclonal antibody to human epidermoid tumor in nude mice.J Nucl Med. 2008 Feb;49(2):295-302. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.046888. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Nucl Med. 2008. PMID: 18199622
-
Combined-modality radioimmunotherapy: synergistic effect of paclitaxel and additive effect of bevacizumab.Nucl Med Biol. 2012 May;39(4):472-83. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2011.10.020. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Nucl Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22172384 Free PMC article.
-
Intralesional radioimmunotherapy with Yttrium-90-labeled human monoclonal IgM in nude mice bearing human tumor xenografts.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2004 Feb;19(1):43-51. doi: 10.1089/108497804773391667. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2004. PMID: 15068610
-
[Radioimmunotherapy with 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan in lymphomas].Rev Esp Med Nucl. 2006 Jan-Feb;25(1):55-68; quiz 69-70.. doi: 10.1157/13083353. Rev Esp Med Nucl. 2006. PMID: 16540015 Review. Spanish. No abstract available.
-
90Yttrium-ibritumomab tiuxetan: a novel treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004 Aug;4(8):1323-31. doi: 10.1517/14712598.4.8.1323. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15268665 Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming physical stromal barriers to cancer immunotherapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Dec;11(6):2430-2447. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-01036-y. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34351575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound ablation enhances drug accumulation and survival in mammary carcinoma models.J Clin Invest. 2016 Jan;126(1):99-111. doi: 10.1172/JCI83312. Epub 2015 Nov 23. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 26595815 Free PMC article.
-
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Enhanced Anti-Tumor Activities of Paclitaxel in Breast Cancer in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Mar 30;14:1303-1312. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S349409. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 35386184 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based assessment of dosing strategies in children for monoclonal antibodies exhibiting target-mediated drug disposition.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 1;3(10):e138. doi: 10.1038/psp.2014.38. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25271939 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed-focused ultrasound enhances boron drug accumulation in a human head and neck cancer xenograft-bearing mouse model.Mol Imaging Biol. 2014 Feb;16(1):95-101. doi: 10.1007/s11307-013-0675-2. Mol Imaging Biol. 2014. PMID: 23925592
References
-
- Allen TM. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:750–763. - PubMed
-
- Koppe MJ, Postema EJ, Aarts F, Oyen WJ, Bleichrodt RP, Boerman OC. Antibody-guided radiation therapy of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005;24:539–567. - PubMed
-
- Yan L, Hsu K, Beckman RA. Antibody-based therapy for solid tumors. Cancer J. 2008;14:178–183. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, Baselga J, Norton L. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:783–792. - PubMed
-
- Jain M, Venkatraman G, Batra SK. Optimization of radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors: biological impediments and their modulation. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1374–1382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

