Bacterial adhesion forces with substratum surfaces and the susceptibility of biofilms to antibiotics
- PMID: 22733073
- PMCID: PMC3421903
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00431-12
Bacterial adhesion forces with substratum surfaces and the susceptibility of biofilms to antibiotics
Abstract
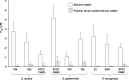
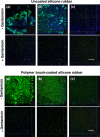
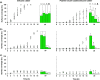
Biofilms causing biomaterial-associated infection resist antibiotic treatment and usually necessitate the replacement of infected implants. Here we relate bacterial adhesion forces and the antibiotic susceptibility of biofilms on uncoated and polymer brush-coated silicone rubber. Nine strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa adhered more weakly to brush-coated silicone rubber (-0.05 ± 0.03 to -0.51 ± 0.62 nN) than to uncoated silicone rubber (-1.05 ± 0.46 to -5.1 ± 1.3 nN). Biofilms of weakly adhering organisms on polymer brush coatings remained in a planktonic state, susceptible to gentamicin, unlike biofilms formed on uncoated silicone rubber.
Figures
References
-
- Andrews JM. 2009. BSAC standardized disc susceptibility testing method (version 8). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 64:454–489 - PubMed
-
- Bolshakova AV, et al. 2001. Comparative studies of bacteria with an atomic force microscopy operating in different modes. Ultramicroscopy 86:121–128 - PubMed
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. 1999. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

