Most colorectal cancer survivors live a large proportion of their remaining life in good health
- PMID: 22733234
- PMCID: PMC3415614
- DOI: 10.1007/s10552-012-0010-2
Most colorectal cancer survivors live a large proportion of their remaining life in good health
Abstract
Purpose: Colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnosis reduces life expectancy and decreases patients' well-being. We sought to assess the determinants of health and functional status and estimate the proportion of remaining life that CRC survivors would spend in good health.
Methods: Using Sullivan method, healthy life expectancy was calculated based on survival data of 14,849 CRC survivors within a population-based cancer registry in southern Netherlands and quality of life information among a random sample of these survivors (n = 1,291).
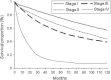
Results: Overall, albeit short life expectancy (LE at age 50 = 12 years for males and 13 years for females), most CRC survivors spent a large proportion of their remaining life in good health (74 and 77 %, for males and females, respectively). Long-term survivors may expect to live a normal life span (LE at age 50 = 30 years) and spent a large proportion of the remaining life in good health (78 %). In distinction, those with stage IV CRC had less than 2 years to live and spent more than half of their remaining life in poor health.
Conclusions: Most CRC patients may expect no compromise on living a healthy life, underlining the importance of early detection. On the other hand, the high proportion of non-healthy years among stage IV CRC survivors confirms the importance of early detection and palliative care.
Figures
References
-
- Shahir MA, Lemmens VE, van de Poll-Franse LV, Voogd AC, Martijn H, Janssen-Heijnen ML. Elderly patients with rectal cancer have a higher risk of treatment-related complications and a poorer prognosis than younger patients: a population-based study. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:3015–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.10.032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical