MicroRNA-30d induces insulin transcription factor MafA and insulin production by targeting mitogen-activated protein 4 kinase 4 (MAP4K4) in pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 22733810
- PMCID: PMC3438947
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.362632
MicroRNA-30d induces insulin transcription factor MafA and insulin production by targeting mitogen-activated protein 4 kinase 4 (MAP4K4) in pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
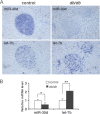
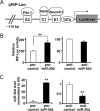
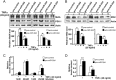
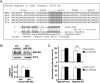
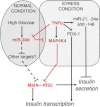
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent small noncoding RNAs that play a role in many diseases, including diabetes. miRNAs target genes important for pancreas development, β-cell proliferation, insulin secretion, and exocytosis. Previously, we documented that microRNA-30d (miR-30d), one of miRNAs up-regulated by glucose, induces insulin gene expression in pancreatic β-cells. Here, we found that the induction of insulin production by overexpression of miR-30d is associated with increased expression of MafA, a β-cell-specific transcription factor. Of interest, overexpression of miR-30d prevented the reduction in both MafA and insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) with TNF-α exposure. Moreover, we identified that mitogen-activated protein 4 kinase 4 (MAP4K4), a TNF-α-activated kinase, is a direct target of miR-30d. Overexpression of miR-30d protected β-cells against TNF-α suppression on both insulin transcription and insulin secretion through the down-regulation of MAP4K4 by the miR-30d. A decrease of miR-30d expression was observed in the islets of diabetic db/db mice, in which MAP4K4 expression level was elevated. Our data support the notion that miR-30d plays multiple roles in activating insulin transcription and protecting β-cell functions from impaired by proinflammatory cytokines and underscore the concept that miR-30d may represent a novel pharmacological target for diabetes intervention.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of glucose-regulated miRNAs from pancreatic {beta} cells reveals a role for miR-30d in insulin transcription.RNA. 2009 Feb;15(2):287-93. doi: 10.1261/rna.1211209. Epub 2008 Dec 18. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19096044 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing mitogen-activated protein 4 kinase 4 (MAP4K4) protects beta cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced decrease of IRS-2 and inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 9;284(41):27892-27898. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.048058. Epub 2009 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19690174 Free PMC article.
-
miR-149 Negative Regulation of mafA Is Involved in the Arsenite-Induced Dysfunction of Insulin Synthesis and Secretion in Pancreatic Beta Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Jan 1;167(1):116-125. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy150. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 29905828
-
PDX1, Neurogenin-3, and MAFA: critical transcription regulators for beta cell development and regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;8(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0694-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and regulation of transcription factor MafA in islet beta-cells.Endocr J. 2007 Dec;54(5):659-66. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.kr-101. Epub 2007 Aug 30. Endocr J. 2007. PMID: 17785922 Review.
Cited by
-
MAP4K4: an emerging therapeutic target in cancer.Cell Biosci. 2016 Oct 28;6:56. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0121-7. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27800153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights regarding the role of noncoding RNAs in diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2023 Jul 15;14(7):958-976. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.958. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37547582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as stress regulators in pancreatic beta cells and diabetes.Mol Metab. 2017 Jul 18;6(9):1010-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.06.020. eCollection 2017 Sep. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28951825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minireview: microRNA function in pancreatic β cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Dec;28(12):1922-33. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1306. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25396300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Effects of Exosomes in Mediating Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;998:113-138. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4397-0_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28936736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

