RelB/NF-κB2 regulates corticotropin-releasing hormone in the human placenta
- PMID: 22734038
- PMCID: PMC5416986
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2012-1035
RelB/NF-κB2 regulates corticotropin-releasing hormone in the human placenta
Abstract
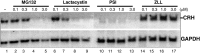
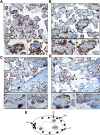
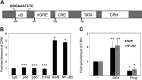
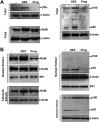
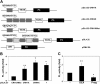
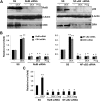
Placental CRH may be part of a clock that governs the length of human gestation. The mechanism underlying differential regulation of CRH in the human placenta is poorly understood. We report here that constitutively activated RelB/nuclear factor-κB2 (NF-κB)-2 (p100/p52) acts as an endogenous stimulatory signal to regulate CRH by binding to an NF-κB enhancer of CRH gene promoter in the human placenta. Nuclear staining of NF-κB2 and RelB in villous syncytiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts was coupled with cytoplasmic CRH in syncytial knots of cytotrophoblasts. Chromatin immunoprecipitation identified that CRH gene associated with both RelB and NF-κB2 (p52). Dexamethasone increased synthesis and nuclear translocation of RelB and NF-κB2 (p52) and their association with the CRH gene. In contrast, progesterone, a down-regulator of placental CRH, repressed NF-κB2 (p100) processing, nuclear translocation of RelB and NF-κB2 (p52), and their association with the CRH gene. Luciferase reporter assay determined that the NF-κB enhancer of CRH was sufficient to regulate transcriptional activity of a heterologous promoter in primary cytotrophoblasts. RNA interference-mediated repression of RelB or NF-κB2 resulted in significant inhibition of CRH at both transcriptional and translational levels and prevented the dexamethasone-mediated up-regulation of CRH transcription and translation. These results suggest that the noncanonical NF-κB pathway regulates CRH production in the human placenta and is responsible for the positive regulation of CRH by glucocorticoids.
Figures
References
-
- Petraglia F , Imperatore A , Challis JR. 2010. Neuroendocrine mechanisms in pregnancy and parturition. Endocr Rev 31:783–816 - PubMed
-
- Petraglia F , Sawchenko PE , Rivier J , Vale W. 1987. Evidence for local stimulation of ACTH secretion by corticotropin-releasing factor in human placenta. Nature 328:717–719 - PubMed
-
- Spaziani EP , O'Brien WF , Benoit RR , Gould SF. 2000. Corticotropin-releasing hormone increases the expression of the prostaglandin E(2) receptor subtype EP1 in amnion WISH cells. Biol Reprod 62:23–26 - PubMed
-
- Li W , Challis JR. 2005. Corticotropin-releasing hormone and urocortin induce secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) without change in tissue inhibitors of MMP-1 by cultured cells from human placenta and fetal membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:6569–6574 - PubMed
-
- Petraglia F , Florio P , Benedetto C , Marozio L , Di Blasio AM , Ticconi C , Piccione E , Luisi S , Genazzani AR , Vale W. 1999. Urocortin stimulates placental adrenocorticotropin and prostaglandin release and myometrial contractility in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:1420–1423 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

