COUP-TFII is a major regulator of cell cycle and Notch signaling pathways
- PMID: 22734039
- PMCID: PMC3404301
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2011-1305
COUP-TFII is a major regulator of cell cycle and Notch signaling pathways
Abstract
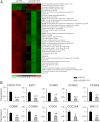
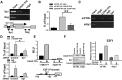
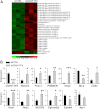
Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF)II has been shown to play a major role in endothelial cell growth and regulation of the Notch signaling pathway to confer vein identity. However, the underlying mechanisms for COUP-TFII regulation in these pathways remain to be defined. Here we employed a genomic approach by using microarray analysis to identify downstream targets in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) cells and found the expression of many genes in the cell cycle pathway and Notch signaling pathway are significantly altered in the COUP-TFII-depleted cells. The expression of E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1), a key transcription factor that regulates the expression of cell cycle regulators, is reduced in the absence of COUP-TFII. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments, we showed that COUP-TFII directly regulates the expression of E2F1 through tethering to the Sp1 binding sites in the promoter of E2F1 to modulate cell proliferation. In addition, we also demonstrate that Foxc1 and Np-1, two upstream genes of Notch signaling and Hey2, a downstream effector of Notch signaling, are direct targets of COUP-TFII. Furthermore, COUP-TFII suppresses the expression of EphrinB2, an arterial marker, while enhancing the expression of ephrin receptor B4, a venous marker, supporting our in vivo findings that COUP-TFII regulates vein identity by suppressing the Notch signal pathway.
Figures
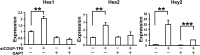

References
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. 2003. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676 - PubMed
-
- Dickson MC, Martin JS, Cousins FM, Kulkarni AB, Karlsson S, Akhurst RJ. 1995. Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-β 1 knock out mice. Development 121:1845–1854 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

