Rapid actions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors regulate motility of mouse embryonic stem cells through a profilin-1/cofilin-1-directed kinase signaling pathway
- PMID: 22734041
- PMCID: PMC5416980
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2012-1002
Rapid actions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors regulate motility of mouse embryonic stem cells through a profilin-1/cofilin-1-directed kinase signaling pathway
Abstract
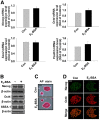
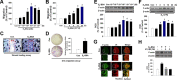
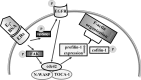
Long-term estrogen actions are vital for driving cell growth, but more recent evidence suggests that estrogen mediates more rapid cellular effects. However, the function of estradiol-17β (E(2))-BSA in mouse embryonic stem cells has not been reported. Therefore, we examined the role of E(2)-BSA in mouse embryonic stem cell motility and its related signal pathways. E(2)-BSA (10(-8) m) significantly increased motility after 24 h incubation and increased filamentous (F)-actin expression; these effects were inhibited by the estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780, indicating that E(2)-BSA bound membrane estrogen receptors and initiated a signal. E(2)-BSA increased c-Src and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation, which was attenuated by ICI 182,780. The E(2)-BSA-induced increase in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) phosphorylation was inhibited by Src inhibitor PP2. As a downstream signal molecule, E(2)-BSA activated cdc42 and increased formation of a complex with the neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP)/cdc42/transducer of cdc42-dependent actin assembly-1 (TOCA-1), which was inhibited by FAK small interfering RNA (siRNA) and EGFR inhibitor AG 1478. In addition, E(2)-BSA increased profilin-1 expression and cofilin-1 phosphorylation, which was blocked by cdc42 siRNA. Subsequently, E(2)-BSA induced an increase in F-actin expression, and cell motility was inhibited by each signal pathway-related siRNA molecule or inhibitors but not by cofilin-1 siRNA. A combined treatment of cofilin-1 siRNA and E(2)-BSA increased F-actin expression and cell motility more than that of E(2)-BSA alone. These data demonstrate that E(2)-BSA stimulated motility by interacting with profilin-1/cofilin-1 and F-actin through FAK- and c-Src/EGFR transactivation-dependent N-WASP/cdc42/TOCA-1 complex.
Figures




References
-
- Park JH , Lee MY , Han HJ. 2009. A potential role for caveolin-1 in estradiol-17β-induced proliferation of mouse embryonic stem cells: involvement of Src, PI3K/Akt, and MAPKs pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:659–665 - PubMed
-
- Yun SP , Lee MY , Ryu JM , Song CH , Han HJ. 2009. Role of HIF-1α and VEGF in human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation by 17β-estradiol: involvement of PKC, PI3K/Akt, and MAPKs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C317–C326 - PubMed
-
- Zhou S , Zilberman Y , Wassermann K , Bain SD , Sadovsky Y , Gazit D. 2001. Estrogen modulates estrogen receptor α and β expression, osteogenic activity, and apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) of osteoporotic mice. J Cell Biochem Suppl 36:144–155 - PubMed
-
- Björnström L , Sjöberg M. 2005. Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol 19:833–842 - PubMed
-
- Keung W , Chan ML , Ho EY , Vanhoutte PM , Man RY. 2011. Non-genomic activation of adenylyl cyclase and protein kinase G by 17β-estradiol in vascular smooth muscle of the rat superior mesenteric artery. Pharmacol Res 64:509–516 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

