Fibroblast circadian rhythms of PER2 expression depend on membrane potential and intracellular calcium
- PMID: 22734566
- PMCID: PMC3491983
- DOI: 10.3109/07420528.2012.679330
Fibroblast circadian rhythms of PER2 expression depend on membrane potential and intracellular calcium
Abstract
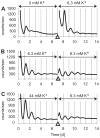
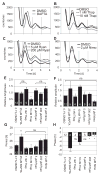
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus synchronizes circadian rhythms of cells and tissues throughout the body. In SCN neurons, rhythms of clock gene expression are suppressed by manipulations that hyperpolarize the plasma membrane or lower intracellular Ca(2+). However, whether clocks in other cells also depend on membrane potential and calcium is unknown. In this study, the authors investigate the effects of membrane potential and intracellular calcium on circadian rhythms in mouse primary fibroblasts. Rhythms of clock gene expression were monitored using a PER2::LUC knockin reporter. Rhythms were lost or delayed at lower (hyperpolarizing) K(+) concentrations. Bioluminescence imaging revealed that this loss of rhythmicity in cultures was due to loss of rhythmicity of single cells rather than loss of synchrony among cells. In lower Ca(2+) concentrations, rhythms were advanced or had shorter periods. Buffering intracellular Ca(2+) by the calcium chelator 1,2-Bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid tetrakis acetoxymethyl ester (BAPTA-AM) or manipulation of inositol triphosphate (IP(3))-sensitive intracellular calcium stores by thapsigargin delayed rhythms. These results suggest that the circadian clock in fibroblasts, as in SCN neurons, is regulated by membrane potential and Ca(2+). Changes in intracellular Ca(2+) may mediate the effects of membrane potential observed in this study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Baxter DF, Kirk M, Garcia AF, Raimondi A, Holmqvist MH, Flint KK, Bojanic D, Distefano PS, Curtis R, Xie Y. A novel membrane potential-sensitive fluorescent dye improves cell-based assays for ion channels. J Biomol Screen. 2002;7:79–85. - PubMed
-
- Chilton L, Ohya S, Freed D, George E, Drobic V, Shibukawa Y, Maccannell KA, Imaizumi Y, Clark RB, Dixon IM, Giles WR. K+ currents regulate the resting membrane potential, proliferation, and contractile responses in ventricular fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H2931–2939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
