Arrow plot: a new graphical tool for selecting up and down regulated genes and genes differentially expressed on sample subgroups
- PMID: 22734592
- PMCID: PMC3542259
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-147
Arrow plot: a new graphical tool for selecting up and down regulated genes and genes differentially expressed on sample subgroups
Abstract
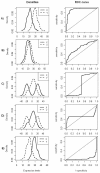
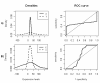
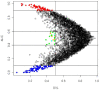
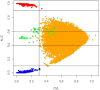
Background: A common task in analyzing microarray data is to determine which genes are differentially expressed across two (or more) kind of tissue samples or samples submitted under experimental conditions. Several statistical methods have been proposed to accomplish this goal, generally based on measures of distance between classes. It is well known that biological samples are heterogeneous because of factors such as molecular subtypes or genetic background that are often unknown to the experimenter. For instance, in experiments which involve molecular classification of tumors it is important to identify significant subtypes of cancer. Bimodal or multimodal distributions often reflect the presence of subsamples mixtures. Consequently, there can be genes differentially expressed on sample subgroups which are missed if usual statistical approaches are used. In this paper we propose a new graphical tool which not only identifies genes with up and down regulations, but also genes with differential expression in different subclasses, that are usually missed if current statistical methods are used. This tool is based on two measures of distance between samples, namely the overlapping coefficient (OVL) between two densities and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The methodology proposed here was implemented in the open-source R software.
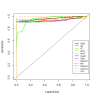
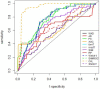
Results: This method was applied to a publicly available dataset, as well as to a simulated dataset. We compared our results with the ones obtained using some of the standard methods for detecting differentially expressed genes, namely Welch t-statistic, fold change (FC), rank products (RP), average difference (AD), weighted average difference (WAD), moderated t-statistic (modT), intensity-based moderated t-statistic (ibmT), significance analysis of microarrays (samT) and area under the ROC curve (AUC). On both datasets all differentially expressed genes with bimodal or multimodal distributions were not selected by all standard selection procedures. We also compared our results with (i) area between ROC curve and rising area (ABCR) and (ii) the test for not proper ROC curves (TNRC). We found our methodology more comprehensive, because it detects both bimodal and multimodal distributions and different variances can be considered on both samples. Another advantage of our method is that we can analyze graphically the behavior of different kinds of differentially expressed genes.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the arrow plot represents a new flexible and useful tool for the analysis of gene expression profiles from microarrays.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

