A review of wide surgical excision of hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 22734714
- PMCID: PMC3407534
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-5945-12-9
A review of wide surgical excision of hidradenitis suppurativa
Abstract
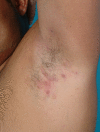
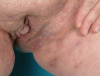
Background: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory cutaneous disorder that involves the infundibular terminal follicles in areas rich of apocrine glands. It can be associated with fistulating sinus, scarring and abscesses formation. Hidradenitis suppurativa is a challenging aspect and requires a proper treatment plan which may involve different specialties. We present herein the option of surgical treatment involving wide surgical excision and methods of reconstruction as well as the rate of recurrence. Furthermore, review of the literature regarding surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa is provided.
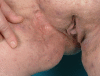
Methods: A retrospective analysis reviewed 50 operative procedures for 32 patients in 5 anatomical sites. These anatomical sites have been divided to 23 sites involving the axilla, 17 sites involving the inguinal region and 8 sites involving the perianal/perineal area, 1 site involving the gluteal region and 1 site involving the trunk region.
Results: Twenty six patients (81, 25 %) showed no recurrence after surgery and the average time of hospital stay period was 5 days. Recurrence was observed only in 6 patients (18, 75 %).
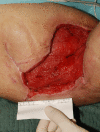
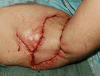
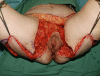
Conclusion: Elimination of the acute inflammatory process should occur in advance, including the use of antibiotics and minor surgeries such as abscess drainage with proper irrigations. After stabilizing the acute phase, wide surgical excision is recommended. Herein, planning of surgical reconstruction should be initiated to achieve the best outcome and consequently decreasing the risk of recurrence and complications after surgery.
Figures



References
-
- Verneuil AS. Etudes sur les tumeurs de la peau et quelques maladies de glandes sudoripares. Arch Gen Med. 1854;94:693–705.
-
- Plewig G, Steger M. Acne inversa (alias acne triad, acne tetrad or hidradenitis suppurativa) Martin Dunitz, London; 1989. pp. 345–57.
-
- Scheinfeld N. Hidradenitis should not be renamed acne inversa. Dermatol. Online J. 2006;12(7):6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

