A high-throughput next-generation sequencing-based method for detecting the mutational fingerprint of carcinogens
- PMID: 22735701
- PMCID: PMC3424585
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks610
A high-throughput next-generation sequencing-based method for detecting the mutational fingerprint of carcinogens
Abstract
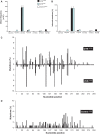
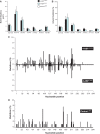
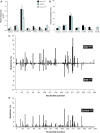
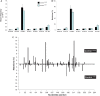
Many carcinogens leave a unique mutational fingerprint in the human genome. These mutational fingerprints manifest as specific types of mutations often clustering at certain genomic loci in tumor genomes from carcinogen-exposed individuals. To develop a high-throughput method for detecting the mutational fingerprint of carcinogens, we have devised a cost-, time- and labor-effective strategy, in which the widely used transgenic Big Blue mouse mutation detection assay is made compatible with the Roche/454 Genome Sequencer FLX Titanium next-generation sequencing technology. As proof of principle, we have used this novel method to establish the mutational fingerprints of three prominent carcinogens with varying mutagenic potencies, including sunlight ultraviolet radiation, 4-aminobiphenyl and secondhand smoke that are known to be strong, moderate and weak mutagens, respectively. For verification purposes, we have compared the mutational fingerprints of these carcinogens obtained by our newly developed method with those obtained by parallel analyses using the conventional low-throughput approach, that is, standard mutation detection assay followed by direct DNA sequencing using a capillary DNA sequencer. We demonstrate that this high-throughput next-generation sequencing-based method is highly specific and sensitive to detect the mutational fingerprints of the tested carcinogens. The method is reproducible, and its accuracy is comparable with that of the currently available low-throughput method. In conclusion, this novel method has the potential to move the field of carcinogenesis forward by allowing high-throughput analysis of mutations induced by endogenous and/or exogenous genotoxic agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Next-Generation Genotoxicology: Using Modern Sequencing Technologies to Assess Somatic Mutagenesis and Cancer Risk.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020 Jan;61(1):135-151. doi: 10.1002/em.22342. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 31595553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct quantification of in vivo mutagenesis and carcinogenesis using duplex sequencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 29;117(52):33414-33425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013724117. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33318186 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling Mutation Spectra of Human Carcinogens Using Experimental Systems.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Sep;121 Suppl 3:16-22. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12690. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27754614 Review.
-
High-throughput sequencing in mutation detection: A new generation of genotoxicity tests?Mutat Res. 2015 Jun;776:136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25934519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational spectra and mutational signatures: Insights into cancer aetiology and mechanisms of DNA damage and repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2018 Nov;71:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30236628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Next-Generation Genotoxicology: Using Modern Sequencing Technologies to Assess Somatic Mutagenesis and Cancer Risk.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020 Jan;61(1):135-151. doi: 10.1002/em.22342. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 31595553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next generation sequencing of benzo(a)pyrene-induced lacZ mutants identifies a germ cell-specific mutation spectrum.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 10;6:36743. doi: 10.1038/srep36743. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27829668 Free PMC article.
-
Benzo(a)pyrene Is Mutagenic in Mouse Spermatogonial Stem Cells and Dividing Spermatogonia.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Aug;152(2):363-71. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw088. Epub 2016 May 13. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27208087 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation Analysis in Cultured Cells of Transgenic Rodents.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 16;19(1):262. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010262. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29337872 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation signatures of carcinogen exposure: genome-wide detection and new opportunities for cancer prevention.Genome Med. 2014 Mar 31;6(3):24. doi: 10.1186/gm541. eCollection 2014. Genome Med. 2014. PMID: 25031618 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeMarini DM. Mutation spectra of complex mixtures. Mutat. Res. 1998;411:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Hussain SP, Harris CC. Molecular epidemiology of human cancer: contribution of mutation spectra studies of tumor suppressor genes. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4023–4037. - PubMed
-
- Besaratinia A, Pfeifer GP. Investigating human cancer etiology by DNA lesion footprinting and mutagenicity analysis. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:1526–1537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

