The distinct and overlapping phenotypic spectra of FOXP1 and FOXP2 in cognitive disorders
- PMID: 22736078
- PMCID: PMC3470686
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-012-1193-z
The distinct and overlapping phenotypic spectra of FOXP1 and FOXP2 in cognitive disorders
Abstract
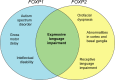
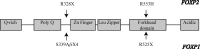
Rare disruptions of FOXP2 have been strongly implicated in deficits in language development. Research over the past decade has suggested a role in the formation of underlying neural circuits required for speech. Until recently no evidence existed to suggest that the closely related FOXP1 gene played a role in neurodevelopmental processes. However, in the last few years, novel rare disruptions in FOXP1 have been reported in multiple cases of cognitive dysfunction, including intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder, together with language impairment. As FOXP1 and FOXP2 form heterodimers for transcriptional regulation, one may assume that they co-operate in common neurodevelopmental pathways through the co-regulation of common targets. Here we compare the phenotypic consequences of FOXP1 and FOXP2 impairment, drawing on well-known studies from the past as well as recent exciting findings and consider what these tell us regarding the functions of these two genes in neural development.
Figures
References
-
- Alarcon M, Abrahams BS, Stone JL, Duvall JA, Perederiy JV, Bomar JM, Sebat J, Wigler M, Martin CL, Ledbetter DH, Nelson SF, Cantor RM, Geschwind DH. Linkage, association, and gene-expression analyses identify CNTNAP2 as an autism-susceptibility gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:150–159. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banham AH, Beasley N, Campo E, Fernandez PL, Fidler C, Gatter K, Jones M, Mason DY, Prime JE, Trougouboff P, Wood K, Cordell JL. The FOXP1 winged helix transcription factor is a novel candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8820–8829. - PubMed
-
- Boucher J (2011) Research review: structural language in autistic spectrum disorder—characteristics and causes. J Child Psychol Psychiatry - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

