Efficient and simultaneous generation of hematopoietic and vascular progenitors from human induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 22736485
- PMCID: PMC3535514
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.22090
Efficient and simultaneous generation of hematopoietic and vascular progenitors from human induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
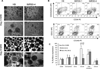
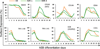
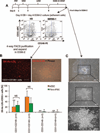
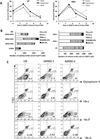
The hematopoietic and vascular lineages are intimately entwined as they arise together from bipotent hemangioblasts and hemogenic endothelial precursors during human embryonic development. In vitro differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells toward these lineages provides opportunities for elucidating the mechanisms of hematopoietic genesis. We previously demonstrated the stepwise in vitro differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESC) to definitive erythromyelopoiesis through clonogenic bipotent primitive hemangioblasts. This system recapitulates an orderly hematopoiesis similar to human yolk sac development via the generation of mesodermal-hematoendothelial progenitor cells that give rise to endothelium followed by embryonic primitive and definitive hematopoietic cells. Here, we report that under modified feeder-free endothelial culture conditions, multipotent CD34⁺ CD45⁺ hematopoietic progenitors arise in mass quantities from differentiated hESC and human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC). These hematopoietic progenitors arose directly from adherent endothelial/stromal cell layers in a manner resembling in vivo hematopoiesis from embryonic hemogenic endothelium. Although fibroblast-derived hiPSC lines were previously found inefficient in hemato-endothelial differentiation capacity, our culture system also supported robust hiPSC hemato-vascular differentiation at levels comparable to hESC. We present comparative differentiation results for simultaneously generating hematopoietic and vascular progenitors from both hESC and fibroblast-hiPSC. This defined, optimized, and low-density differentiation system will be ideal for direct single-cell time course studies of the earliest hematopoietic events using time-lapse videography, or bulk kinetics using flow cytometry analyses on emerging hematopoietic progenitors.
Copyright © 2012 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Figures

References
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA, Ruotti V, Stewart R, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
-
- Lengerke C, Daley GQ. Disease models from pluripotent stem cells. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2009;1176:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Grskovic M, Javaherian A, Strulovici B, Daley GQ. Induced pluripotent stem cells—Opportunities for disease modelling and drug discovery. Nature reviews. Drug Discov. 2011;10:915–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

