Oligodendroglia are limited in type I interferon induction and responsiveness in vivo
- PMID: 22736486
- PMCID: PMC3422432
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.22375
Oligodendroglia are limited in type I interferon induction and responsiveness in vivo
Abstract
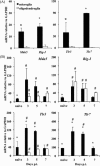
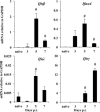
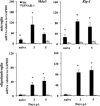
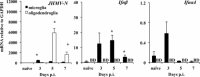
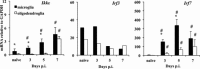
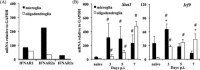
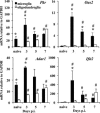
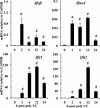
Type I interferons (IFNα/β) provide a primary defense against infection. Nevertheless, the dynamics of IFNα/β induction and responsiveness by central nervous system (CNS) resident cells in vivo in response to viral infections are poorly understood. Mice were infected with a neurotropic coronavirus with tropism for oligodendroglia and microglia to probe innate antiviral responses during acute encephalomyelitis. Expression of genes associated with the IFNα/β pathways was monitored in microglia and oligodendroglia purified from naïve and infected mice by fluorescent activated cell sorting. Compared with microglia, oligodendroglia were characterized by low basal expression of mRNA encoding viral RNA sensing pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), IFNα/β receptor chains, interferon sensitive genes (ISG), as well as kinases and transcription factors critical in IFNα/β signaling. Although PRRs and ISGs were upregulated by infection in both cell types, the repertoire and absolute mRNA levels were more limited in oligodendroglia. Furthermore, although oligodendroglia harbored higher levels of viral RNA compared with microglia, Ifnα/β was only induced in microglia. Stimulation with the double stranded RNA analogue poly I:C also failed to induce Ifnα/β in oligodendroglia, and resulted in reduced and delayed induction of ISGs compared with microglia. The limited antiviral response by oligodendroglia was associated with a high threshold for upregulation of Ikkε and Irf7 transcripts, both central to amplifying IFNα/β responses. Overall, these data reveal that oligodendroglia from the adult CNS are poor sensors of viral infection and suggest they require exogenous IFNα/β to establish an antiviral state.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of class I antigen processing components in oligodendroglia and microglia during viral encephalomyelitis.Glia. 2008 Mar;56(4):426-35. doi: 10.1002/glia.20625. Glia. 2008. PMID: 18205173 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha/Beta Interferon (IFN-α/β) Signaling in Astrocytes Mediates Protection against Viral Encephalomyelitis and Regulates IFN-γ-Dependent Responses.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e01901-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01901-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29491163 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Ablation of Alpha/Beta Interferon (IFN-α/β) Signaling Exacerbates Central Nervous System Viral Dissemination and Impairs IFN-γ Responsiveness in Microglia/Macrophages.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e00422-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00422-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32796063 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular Communication Is Key for Protective IFNα/β Signaling During Viral Central Nervous System Infection.Viral Immunol. 2019 Jan/Feb;32(1):1-6. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0101. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Viral Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30222502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of IPS-1 in type I IFN induction].Nihon Rinsho. 2006 Jul;64(7):1231-5. Nihon Rinsho. 2006. PMID: 16841392 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The role of type I IFN in autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases with CNS involvement.Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1026449. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1026449. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36438941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keeping it in check: chronic viral infection and antiviral immunity in the brain.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Dec;17(12):766-776. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.140. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27811921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ifit2 deficiency results in uncontrolled neurotropic coronavirus replication and enhanced encephalitis via impaired alpha/beta interferon induction in macrophages.J Virol. 2014 Jan;88(2):1051-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02272-13. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24198415 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct CD4 T-cell effects on primary versus recall CD8 T-cell responses during viral encephalomyelitis.Immunology. 2015 Mar;144(3):374-386. doi: 10.1111/imm.12378. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25187405 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking down the cellular responses to type I interferon neurotoxicity in the brain.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 3;14:1110593. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1110593. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akwa Y,Hassett DE,Eloranta ML,Sandberg K,Masliah E,Powell H,Whitton JL,Bloom FE,Campbell IL. 1998. Transgenic expression of IFN‐alpha in the central nervous system of mice protects against lethal neurotropic viral infection but induces inflammation and neurodegeneration. J Immunol 161: 5016–5026. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L,Holt AC,Medzhitov R,Flavell RA. 2001. Recognition of double‐stranded RNA and activation of NF‐kappaB by Toll‐like receptor 3. Nature 413: 732–738. - PubMed
-
- Bass BL. 1997. RNA editing and hypermutation by adenosine deamination. Trends Biochem Sci 22: 157–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

