Flow cytometry analysis of murine hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 22736515
- PMCID: PMC3638885
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.22093
Flow cytometry analysis of murine hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
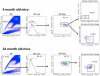
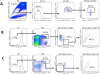
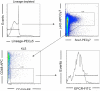
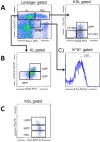
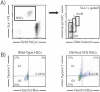
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) remain the most well-characterized adult stem cell population both in terms of markers for purification and assays to assess functional potential. However, despite over 40 years of research, working with HSCs in the mouse remains challenging because of the relative abundance (or lack thereof) of these cells in the bone marrow. The frequency of HSCs in murine bone marrow is about 0.01% of total nucleated cells and ∼5,000 can be isolated from an individual mouse depending on the age, sex, and strain of mice as well as purification scheme utilized. Adding to the challenge is the continual reporting of new markers for HSC purification, which makes it difficult for the uninitiated in the field to know which purification strategies yield the highest proportion of long-term, multilineage HSCs. In this updated version of our review from 2009, we review different strategies for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell identification and purification. We will also discuss methods for rapid flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood cell types, and novel strategies for working with rare cell populations such as HSCs in the analysis of cell cycle status by BrdU, Ki-67, and Pyronin Y staining. The purpose of updating this review is to provide insight into some of the recent experimental and technical advances in mouse hematopoietic stem cell biology.
Copyright © 2012 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Figures


References
-
- Adolfsson J, et al. Upregulation of Flt3 expression within the bone marrow Lin(−)Sca1(+)c-kit(+) stem cell compartment is accompanied by loss of self-renewal capacity. Immunity. 2001;15(4):659–69. - PubMed
-
- Kiel MJ, Radice GL, Morrison SJ. Lack of evidence that hematopoietic stem cells depend on N-cadherin-mediated adhesion to osteoblasts for their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(2):204–17. - PubMed
-
- Zhou S, et al. The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat Med. 2001;7(9):1028–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 DK092883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000183/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK092883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL092332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR017895/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008307/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL092332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG034451/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2AG036562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR021054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

