Rapid uptake and degradation of CXCL12 depend on CXCR7 carboxyl-terminal serine/threonine residues
- PMID: 22736769
- PMCID: PMC3436560
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335679
Rapid uptake and degradation of CXCL12 depend on CXCR7 carboxyl-terminal serine/threonine residues
Abstract
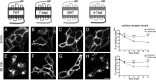
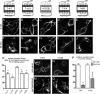
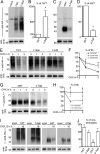
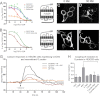
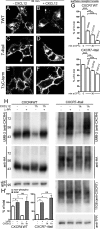
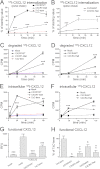
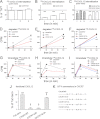
CXCL12 signaling through G protein-coupled CXCR4 regulates cell migration during ontogenesis and disease states including cancer and inflammation. The second CXCL12-receptor CXCR7 modulates the CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway by acting as a CXCL12 scavenger and exerts G protein-independent functions. Given the distinct properties of CXCR4 and CXCR7, we hypothesized that the distinct C-terminal domains differently regulate receptor trafficking and stability. Here, we examined epitope-tagged wild type and C-terminal mutant receptors in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) with respect to trafficking, stability, (125)I-CXCL12 degradation, and G protein-coupling. The 24 CXCR7 C-terminal residues were sufficient to promote rapid spontaneous internalization. Replacement of the CXCR7 C terminus with that of CXCR4 (CXCR7-4tail mutant) abolished spontaneous internalization but permitted ligand-induced internalization and phosphorylation at the heterologous domain. The reverse tail-swap caused ligand-independent internalization of the resulting CXCR4-7tail mutant. Receptor-mediated (125)I-CXCL12 uptake and release of (125)I-CXCL12 degradation products were accelerated with receptors bearing the CXCR7 C terminus and impaired after conversion of CXCR7 C-terminal serine/threonine residues into alanines. C-terminal lysine residues were dispensable for plasma membrane targeting and the CXCL12 scavenger function but involved in constitutive degradation of CXCR7. Although the CXCR7 C terminus abolished G protein coupling in the CXCR4-7tail mutant, replacement of the CXCR7 C terminus, CXCR7 second intracellular loop, or both domains with the corresponding CXCR4 domain did not result in a G protein-coupled CXCR7 chimera. Taken together, we provide evidence that the CXCR7 C terminus influences the ligand-uptake/degradation rate, G protein coupling, and receptor stability. Regulatory pathways targeting CXCR7 C-terminal serine/threonine sites may control the CXCL12 scavenger activity of CXCR7.
Figures
References
-
- Sierro F., Biben C., Martínez-Muñoz L., Mellado M., Ransohoff R. M., Li M., Woehl B., Leung H., Groom J., Batten M., Harvey R. P., Martínez-A C., Mackay C. R., Mackay F. (2007) Disrupted cardiac development but normal hematopoiesis in mice deficient in the second CXCL12/SDF-1 receptor, CXCR7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 14759–14764 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zou Y. R., Kottmann A. H., Kuroda M., Taniuchi I., Littman D. R. (1998) Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in hematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 393, 595–599 - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa T., Hirota S., Tachibana K., Takakura N., Nishikawa S., Kitamura Y., Yoshida N., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T. (1996) Defects of B-cell lymphopoiesis and bone-marrow myelopoiesis in mice lacking the CXC chemokine PBSF/SDF-1. Nature 382, 635–638 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

