Dual super-systolic core for real-time reconstructive algorithms of high-resolution radar/SAR imaging systems
- PMID: 22736964
- PMCID: PMC3376574
- DOI: 10.3390/s120302539
Dual super-systolic core for real-time reconstructive algorithms of high-resolution radar/SAR imaging systems
Abstract
A high-speed dual super-systolic core for reconstructive signal processing (SP) operations consists of a double parallel systolic array (SA) machine in which each processing element of the array is also conceptualized as another SA in a bit-level fashion. In this study, we addressed the design of a high-speed dual super-systolic array (SSA) core for the enhancement/reconstruction of remote sensing (RS) imaging of radar/synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensor systems. The selected reconstructive SP algorithms are efficiently transformed in their parallel representation and then, they are mapped into an efficient high performance embedded computing (HPEC) architecture in reconfigurable Xilinx field programmable gate array (FPGA) platforms. As an implementation test case, the proposed approach was aggregated in a HW/SW co-design scheme in order to solve the nonlinear ill-posed inverse problem of nonparametric estimation of the power spatial spectrum pattern (SSP) from a remotely sensed scene. We show how such dual SSA core, drastically reduces the computational load of complex RS regularization techniques achieving the required real-time operational mode.
Keywords: FPGA; parallel computing; remote sensing; super-systolic.
Figures


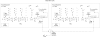


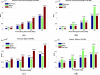
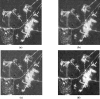
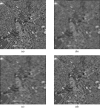
References
-
- Martínez D.R., Bond R.A., Vai M.M. High Performance Embedded Computing Handbook: A Systems Perspective. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2008.
-
- Levesque J., Wagenbreth G. High Performance Computing Programming and Applications. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2011.
-
- Henderson F.M., Lewis A.V. Principles and Applications of Imaging Radar, Manual of Remote Sensing. 3rd ed. Wiley; New York, NY, USA: 1998.
-
- Barrett H.H., Myers K.J. Foundations of Image Science. Wiley; New York, NY, USA: 2004.
-
- Chang C.-I. Hyperspectral Imaging: Techniques for Spectral Detectionand Classification. Kluwer Academic/Plenum; New York, NY, USA: 2003.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

